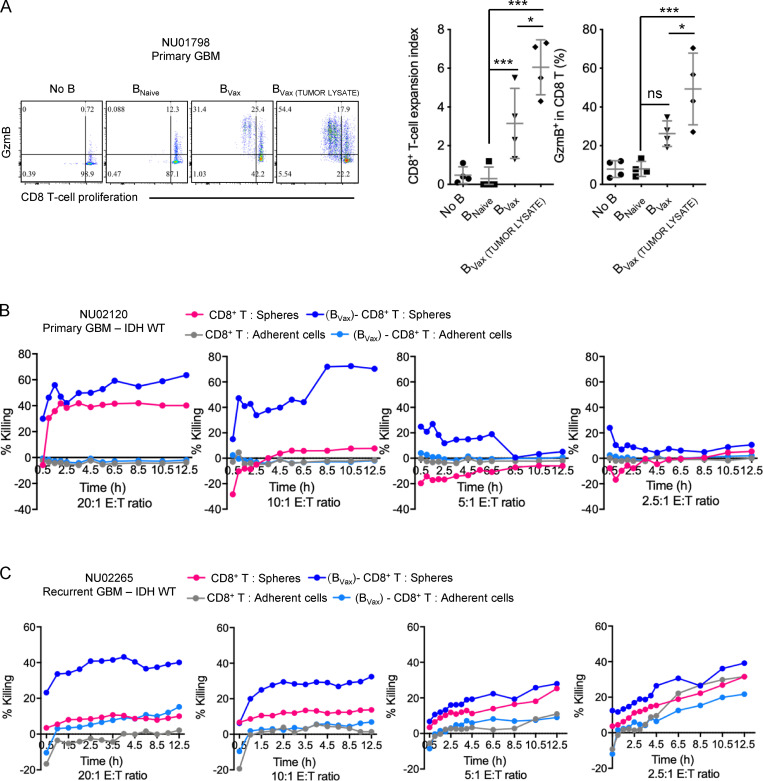
Figure 7.
GBM patient-derived BVax promote anti-tumor CD8+ T cells. (A) Paired fresh peripheral blood and tumor were collected from newly diagnosed GBM patients (n = 4). BVax were generated and pulsed with tumor lysates and co-cultured with autologous eFluor450-labeled CD8+ T cells. CD8+ T cell activation was assessed by cell proliferation (eFluor450 fluorescence dilution measured as expansion index) and intracellular expression of GzmB. (B and C) Paired samples from primary GBM isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) WT (case NU 02120, B) and recurrent GBM IDH WT (NU02265, C). BVax-activated autologous CD8+ T cells (effector cells; E) were obtained as shown in A and tested for their ability to kill autologous glioma cells (target cells; T). Cell killing measurements were taken periodically for 12.5 h using the IncuCyte S3 Live Cell Analysis System. Differences among multiple groups were evaluated using one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's test followed by post hoc Dunn's multiple tests. Histograms are shown as mean ± SD. Statistical significance is depicted as follows: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. ns, not statistically significant.