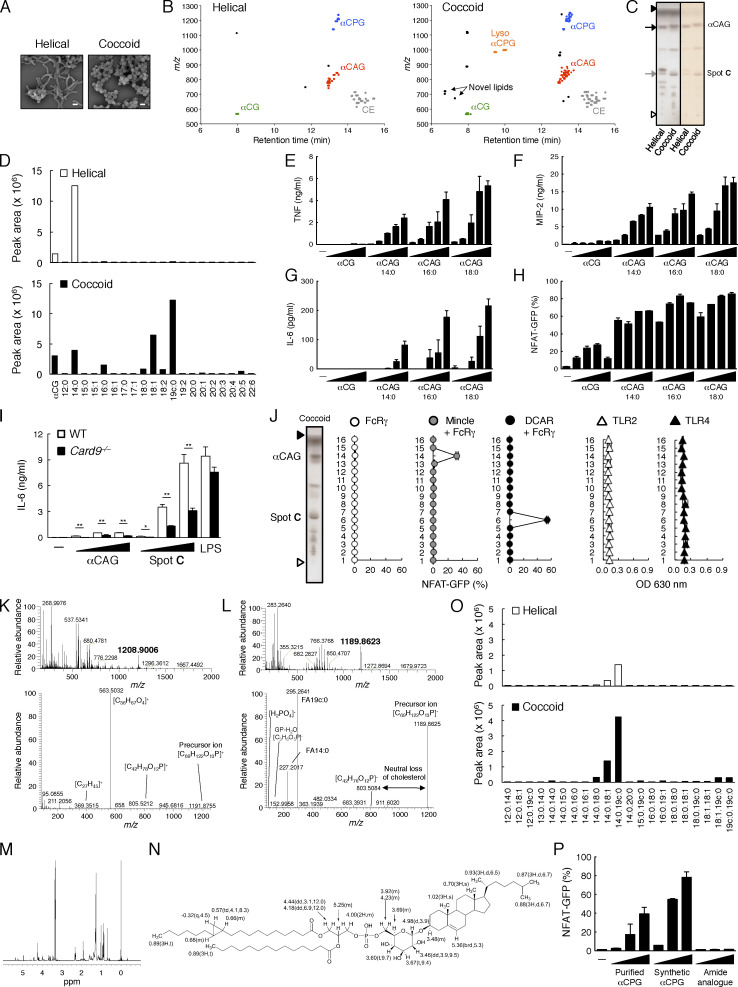
Figure 4.
Nontargeted lipidomics of H. pylori revealed the regulation of immunostimulatory potential by changing lipid composition. (A) Scanning electron micrographs of helical form and coccoid form of H. pylori. Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) 2D map of mass (m/z of precursor ions) versus liquid chromatography retention time of cholesteryl lipids isolated from helical (left panel) or coccoid (right panel) form of H. pylori. Plots of precursor ions were identified as cholesterol ester (CE), αCG, αCAG, αCPG, and lyso αCPG (detected only in coccoid form). (C) Lipid extracts from helical or coccoid form of H. pylori were analyzed by HPTLC using chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4, vol/vol/vol) and stained with copper(II) acetate-phosphoric acid (left) or orcinol (right). Open and closed arrowheads denote the origin and the solvent front, respectively. The black arrow indicates αCAG, and the gray arrow indicates the lipid component increasing in coccoid form (Spot C). (D) Peak area of each fatty acid fragment ion of αCAG that is analyzed in Fig. S3 C. (E–G) BMDCs were stimulated with αCG, αCAG C14:0, C16:0, or C18:0 (0.02, 0.06, 0.2, 0.6, and 2 nmol/well) for 1 d. The concentrations of TNF (E), MIP-2 (F), and IL-6 (G) in the supernatants were determined by ELISA. (H) Reporter cells expressing Mincle + FcRγ were stimulated with αCG, αCAG C14:0, C16:0, or C18:0 (0.016, 0.08, 0.4 and 2 nmol/well) for 20 h and analyzed for GFP expression. (I) Resident peritoneal exudate cells from WT or Card9−/− mice were stimulated with αCAG C14:0, Spot C (0.02, 0.2, and 2 nmol/well) or LPS. IL-6 production was quantified by ELISA. (J) NFAT-GFP reporter cells expressing FcRγ alone, Mincle + FcRγ or DCAR + FcRγ or HEK-based NF-κB reporter cells expressing TLR2 or TLR4 were stimulated with HPTLC-separated lipids from coccoid H. pylori for 20 h and analyzed for GFP or SEAP expression. (K) Full scan MS spectra of Spot C(upper panel) and MS/MS spectra of m/z 1208.9006 [M+NH4]+ (lower panel) in the positive ion mode. Ion peak at m/z 1208.9006 [M + NH4]+ is proposed to be cholesteryl α-phosphatidylpyranoside (calculated mass, 1208.9040). (L) Full-scan MS spectra of Spot C (upper panel) and MS/MS spectra of m/z 1189.8623 [M-H]− (lower panel) in the negative ion mode. Ion peak at m/z 1189.8623 [M-H]− is supposed to be cholesteryl α-phosphatidylpyranoside (calculated mass, 1189.8629). (M) 1H-NMR spectrum (600 MHz, CDCl3:CD3OD:D2O [65:35:5], 298 K) of Spot C. (N) Chemical structure and 1H-NMR chemical shifts assignment of Spot C. Chemical shifts are given in δ ppm, followed by integration, multiplicity and J in hertz. (O) Peak area of each fatty acid fragment ion of αCPG that is analyzed in Fig. S3 D. (P) Reporter cells expressing DCAR + FcRγ were stimulated with purified αCPG, synthesized αCPG (C14:0 19c:0) or αCPG amide analogue (0.1, 0.3 and 1 nmol/well) for 20 h and analyzed for GFP expression. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate (E–G and I) or duplicate (H, J, and P) assays and are representative of two independent experiments. An unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was used for the statistical analyses. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.