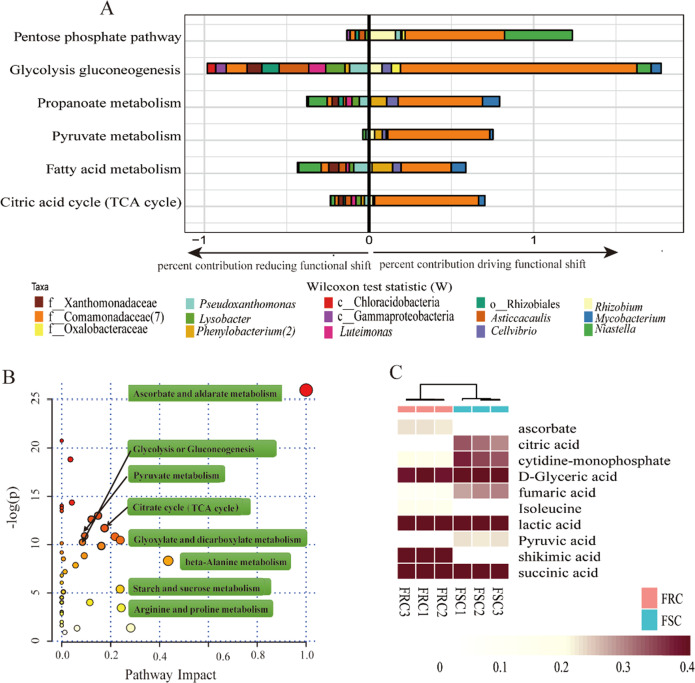
Fig. 3. Prediction of the major pathways mediated by microbial communities and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of root exudates between two cultivars.
a To identify the shifts in rhizosphere communities caused by these potential beneficial bacteria enriched in the Foc-susceptible cultivar rhizosphere, deconvolution of significant community-wide functional shifts into individual taxonomic contributions was performed. The right bar plot represents relative contributions driving functional shifts by the taxa of Foc-susceptible samples, and the left bar plot represents relative contributions reducing functional shifts by the taxa of Foc-susceptible samples. b Different metabolic pathways of the root exudates of two cucumber cultivars. Each point represents a different metabolic pathway, and the size of each point represents the degree of change in each metabolic pathway. c Heatmap analysis of 10 compounds selected by PCA, random forest classification, and pathway enrichment analyses; these compounds were significantly (t-test, p<0.05) different in terms of their relative abundance between the root exudates of the two cucumber cultivars.