Figure 4.
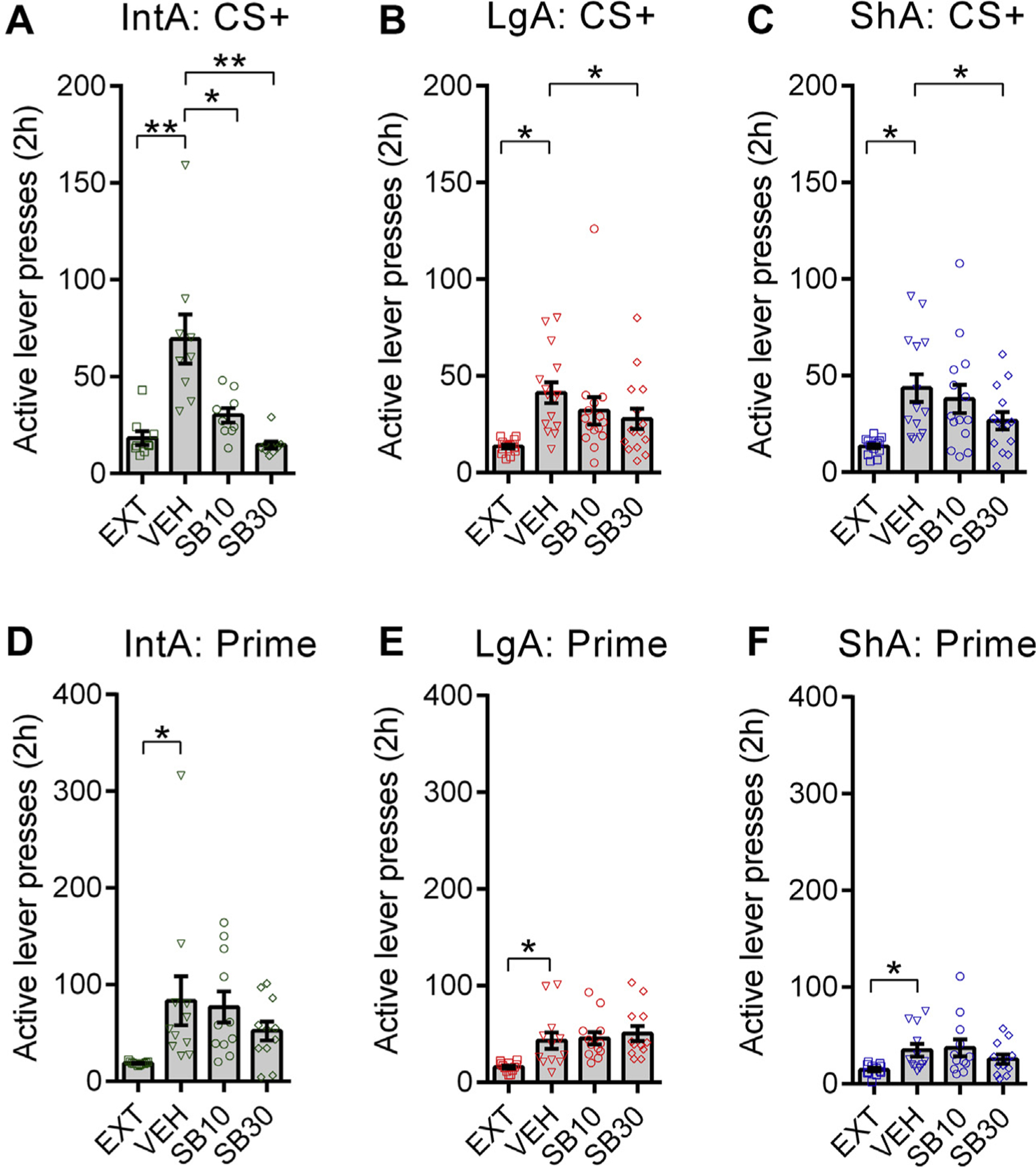
SB-334867 (SB) blocks cued reinstatement at a lower dose in intermittent access (IntA) animals. (A) IntA rats showed robust cued reinstatement behavior (F3,35 = 14.03, p = .0038, overall analysis of variance [ANOVA]). SB10 (t8 = 2.750, p = .0250; Holm-Sidak post hoc test) and SB30 (t8 = 4.128, p = .0066; Holm-Sidak post hoc test) significantly reduced cued reinstatement of active lever responding in IntA animals. n = 9 for all tests. (B) Long access (LgA) rats also showed cued reinstatement behavior (F3,59 = 5.772, p = .0068, overall ANOVA). Only SB30 was significantly effective at reducing reinstatement in LgA rats (t14 = 2.147, p = .0498; Holm-Sidak post hoc test). n = 15 for all tests. (C) Short access (ShA) animals showed cued reinstatement behavior (F3,55 = 8.510, p = .0008, overall ANOVA). Only SB30 significantly reduced reinstatement in ShA rats (t13 = 2.930, p = .0233; Holm-Sidak post hoc test). n = 14 for all tests. (D–F) A priming dose (10 mg/kg) of cocaine elicited reinstatement of active lever responding (relative to levels of pooled extinction values across all groups [EXT]) in IntA (F3,43 = 3.433, p = .0259, overall ANOVA; t10 = 2.887, p = .0186, Holm-Sidak post hoc comparison), LgA (F3,47 = 7.297, p = .0027, overall ANOVA; t11 = 3.152, p = .0274, Holm-Sidak post hoc comparison), and ShA (F3,47 = 4.013, p = .0291, overall ANOVA; t11 = 3.196, p = .0253, Holm-Sidak post hoc comparison) rats. Across all groups, SB had no effect on active lever responding during these tests. IntA, n = 11; LgA, n = 12; ShA, n = 12 for all tests. Holm-Sidak post hoc comparisons. Error bars are SEM. CS+, conditioned stimulus 1; VEH, vehicle. *p < .05; **p < .01.
