Fig. 5 |. Single-cell multiomics approaches for cardiovascular precision medicine.
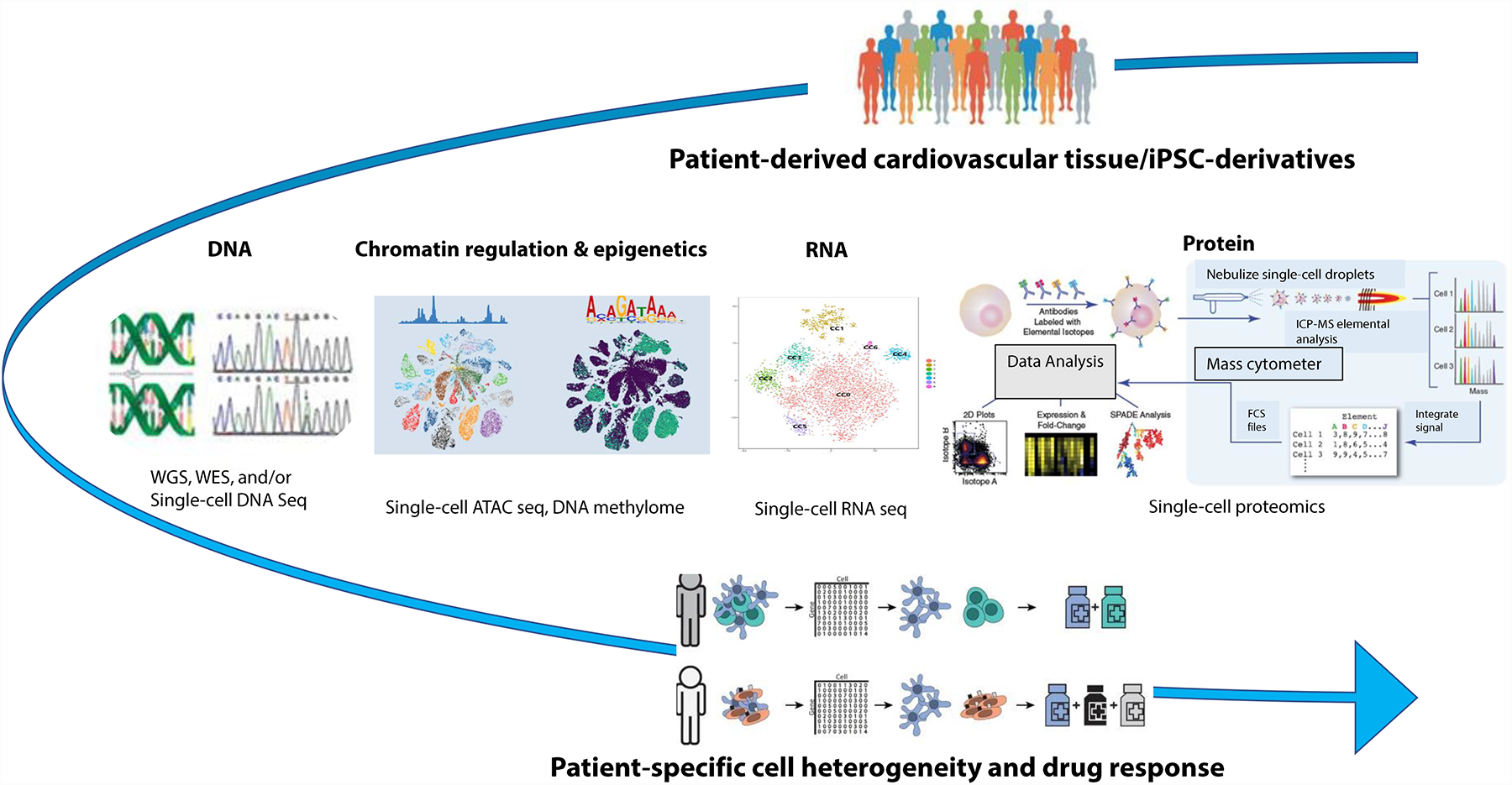
To date, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) has been used most effectively to identify novel or rare cell populations, to confirm the cellular heterogeneity of the tissue or organ of interest, and to construct cell trajectory of developmental or differentiation processes. The increasing and expected technical advances in single-cell analyses of other macromolecules present a unique opportunity to combine multiple single-cell omics approaches149 to advance cardiovascular precision medicine. In addition to single-cell genomics and transcriptomics, single-cell chromatin accessibility, DNA methylome and proteomics will improve our ability to understand cellular heterogeneity unique to each individual, allowing us to better predict the individual-specific responses to cardiovascular drugs and therapies. CITE-seq, cellular indexing of transcriptomes and epitopes by sequencing; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; LC-MS, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; MS, mass spectrometry; scATAC-seq, single-cell assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing; WES, whole-exome sequencing; WGS, whole-genome sequencing.
