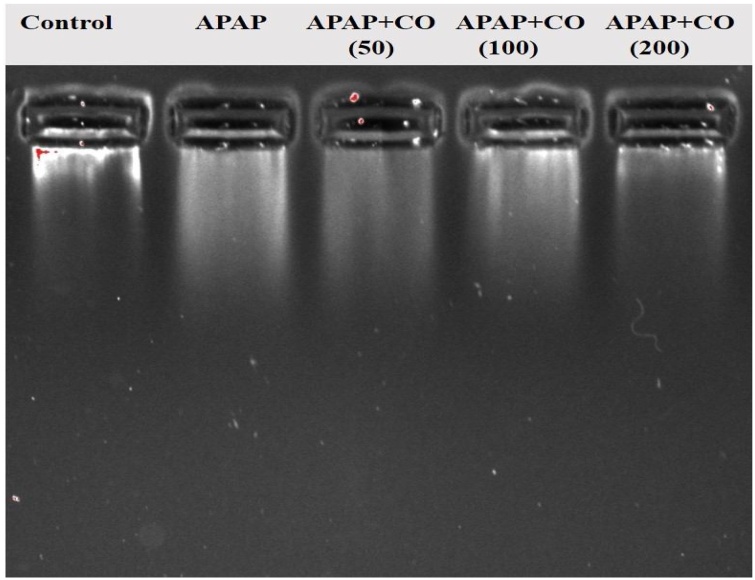
Fig. 12.
Effects of CO on APAP-Induced genomic DNA fragmentation in the liver. Electrophoresis analysis demonstrates that APAP induced considerable cleavage of DNA into smaller fragments including a smear similar to ones seen during apoptotic cell death, and a substantial reduction in DNA damage with CO treatment. Each lane contains liver DNA (mitochondrial + nuclear: 100 ng/lane) extracted collectively from four treated or untreated livers. Lanes represent as follows: Lane-1: vehicle treated control; lane-2: APAP alone; lane-3 APAP + CO (50 mg); lane-4: APAP + CO (100 mg); lane-5: APAP + CO (200 mg).