Figure 1.
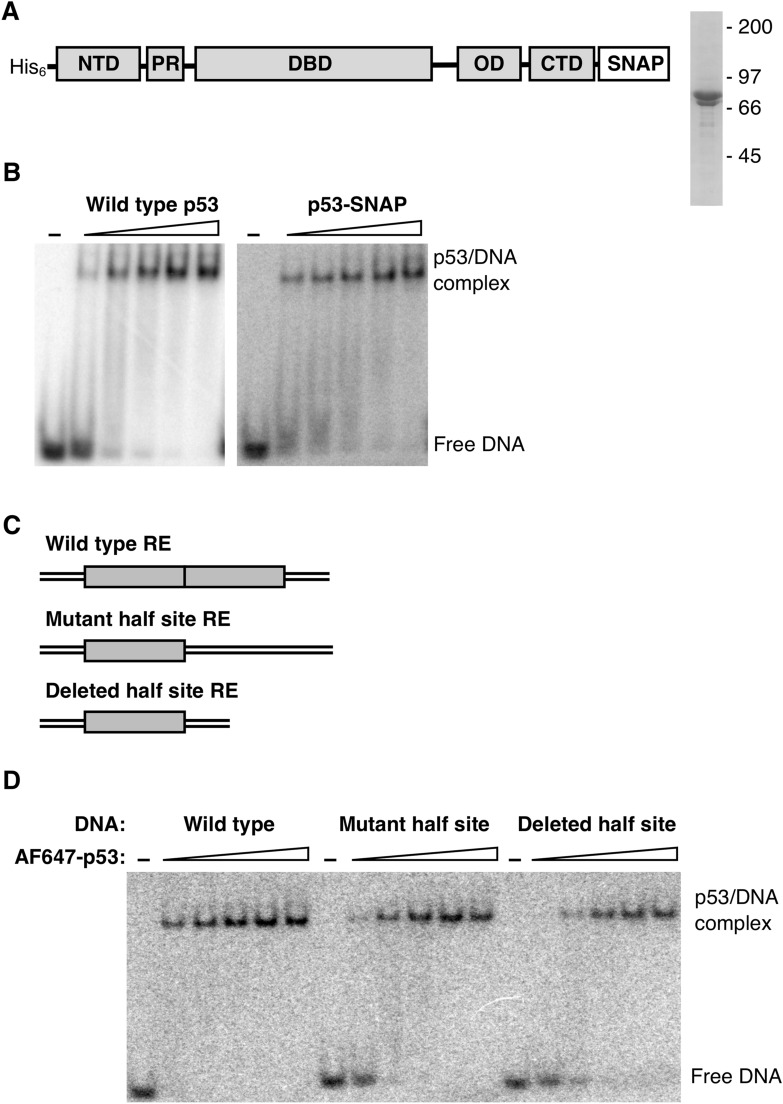
Full length p53 labeled with AF647 via a SNAP tag binds DNA with sub-nM affinity in EMSAs. (A) Schematic showing the domain structure of human full length p53 with the His tag used for purification and the SNAP tag used for fluorescent labeling. Also shown is the purified protein resolved by SDS-PAGE. The positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated; the less abundant band is protein lacking the His tag. An uncropped image of the gel is shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. The abbreviations are as follows: NTD, N-terminal domain; PR, proline-rich domain; DBD, DNA binding domain; OD, oligomerization domain; CTD, C-terminal domain. (B) The addition of a C-terminal SNAP tag to full length p53 does not appreciably alter DNA binding activity. The wild type p53 and p53-SNAP titrations were as follows (maximal tetramer concentrations): 0.025, 0.075, 0.25, 0.75, and 2.5 nM. In all experiments p53 concentrations are expressed as maximum tetrameric concentration, given the monomer concentrations added to the assays. Uncropped images of the gels are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7. (C) Schematics showing the half site composition of the p53 REs tested. The wild type 32 bp DNA is from the GADD45 promoter and consists of two 10 bp half sites (gray boxes) with no spacing between them. The mutant half site DNA was the same length (32 bp) and had one half site scrambled, whereas the deleted half site DNA had one half site removed and was therefore shorter (22 bp). (D) p53 binds DNA containing one or two half sites with high affinity and the same oligomeric state. The AF647-p53 titration was as follows (maximal tetramer concentration): 0.075, 0.25, 0.75, 2.5, and 7.5 nM. An uncropped image of the gel is shown in Supplementary Fig. 7.