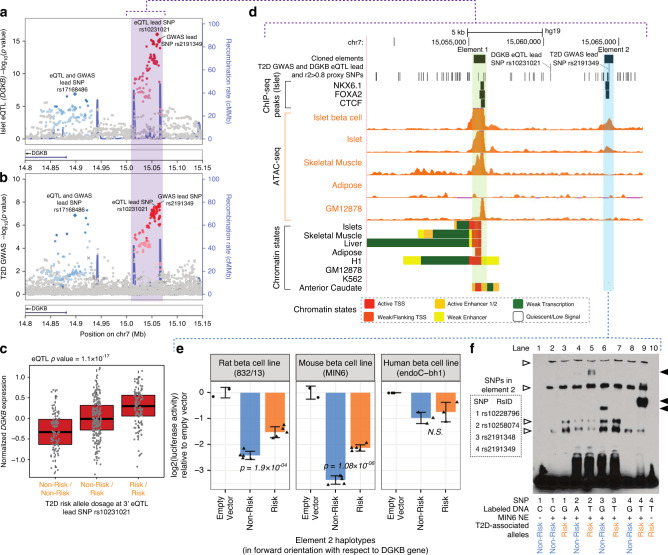
Fig. 4. Functional assessment of DGKB eQTL locus.
a We show the two of the three independent islet eQTL signals that colocalize with identified independent GWAS variants near the DGKB gene locus (lead SNP rs17168486 referred at as the 5′ signal and lead SNP rs10231021 referred to as the 3′ signal). These signals colocalize with two independent T2D GWAS signals shown in b, where rs17168486 is referred to as the 5′ signal and lead SNP rs2191349 referred to as the 3′ signal. LD information was not available for SNPs denoted by (×). The third GWAS variant and the third eSNP are not shown as both are located outside this region and in opposite location with respect to DGKB, showing no evidence of colocalization. c Normalized DGKB gene expression levels relative to the T2D-risk-allele dosage at the 3′ islet eQTL for DGKB lead SNP rs10231021. eQTL p-value adjusted to the beta distribution is shown. d Genome browser view of the region highlighted in purple in a and b that contains the 3′ DGKB eQTL and T2D GWAS signals. Two regulatory elements (element 1 highlighted in green, element 2 highlighted in blue) overlapping ATAC-seq peaks in islet β-cells (islet single nuclei ATAC-seq49) and bulk islets (islet track represents one islet sample from Varshney et al.15) were cloned into a luciferase reporter assay construct for functional validation. All ATAC-seq tracks are normalized to 10 M reads and scaled from 0–15. e Log 2 luciferase assay activities (normalized to empty vector) are shown for in rat (832/13), mouse (MIN6), and human (EndoC-βH1) β-cell lines for the element 2 (cloned in the forward orientation), highlighted in blue in d. The risk haplotype shows significantly higher (p < 0.05) activity than the non-risk haplotype in 832/13 and MIN6, consistent with the eQTL direction shown in c. P-values were determined using unpaired two-sided t-tests. f EMSA for probes with risk and non-risk alleles at the four SNPs overlapping the regulatory element validated in e, using nuclear extract from MIN6 cells. Filled arrows, allele-specific binding; open arrows, non-allele-specific binding of proteins to probes. Source data are provided as a Source data file.