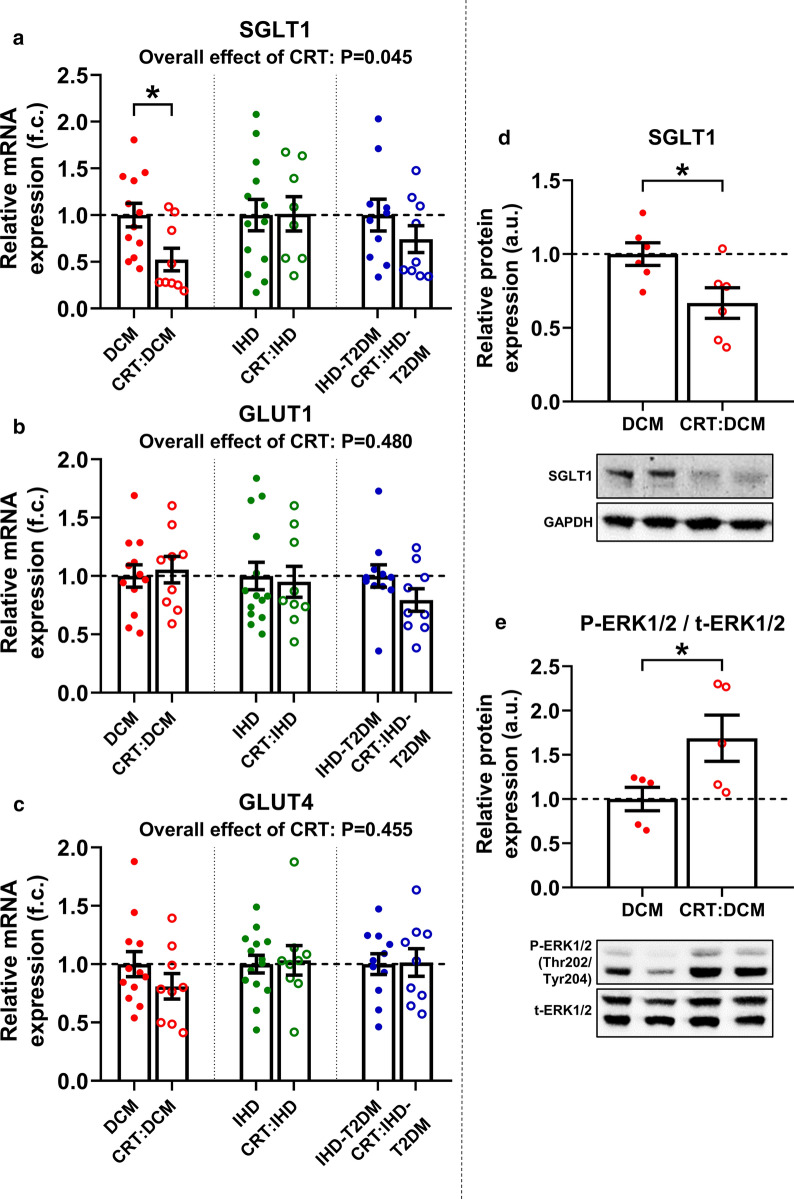
Fig. 5.
Effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy on left ventricular expression of the three major glucose transporters. a Comparison of left ventricular (LV) relative mRNA expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 1 (SGLT1) between heart failure (HF) patients with and without cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). b Comparison of LV relative mRNA expression of facilitative glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) between HF patients with and without CRT. c Comparison of LV relative mRNA expression of GLUT4 between HF patients with and without CRT. d Relative protein expression of LV SGLT1 in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with and without CRT. A representative blot is depicted. e Phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (P-ERK1/2) versus total ERK1/2 (t-ERK1/2) protein expressions in patients with DCM with and without CRT. A representative blot is depicted. For easier interpretation, expression values are normalized to that of non-CRT groups within each etiological subgroup (i.e. mean of corresponding non-CRT group = 1.00). Point-biserial correlation analysis on ranked scores was performed to compute the overall effect of CRT on LV mRNA expression of target genes, the related P values are reported. Significance of difference between two groups was assessed using unpaired Student t-test with Welch’s correction. Accordingly, statistical significance is highlighted as: *P < 0.05. a.u. arbitrary units, CRT cardiac resynchronization therapy, DCM dilated cardiomyopathy, f. c. fold change, ERK1/2 extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, GAPDH glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GLUT1 and 4 facilitative glucose transporter 1 and 4, HCM hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, IHD ischemic heart disease, IHD-T2DM IHD and type 2 diabetes mellitus, SGLT1 sodium-glucose cotransporter 1