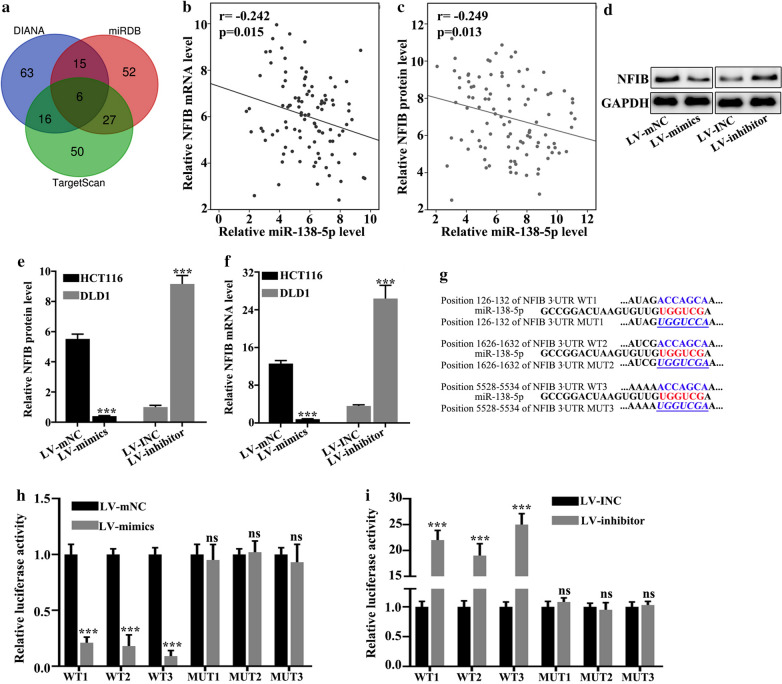
Fig. 5.
miR-138-5p targeted NFIB. a Target genes of miR-138-5p were predicted by three databases, and NFIB was screened out based on biological function. b Relative NFIB mRNA level negatively correlated with relative miR-138-5p level (r = − 0.242, p < 0.05). c Relative NFIB protein level negatively correlated with relative miR-138-5p level (r = − 0.249, p < 0.05). d NFIB protein expression in stable cell lines. e In HCT116 cell lines, LV-mimics group was lower in the expression of NFIB protein than LV-mNC group (p < 0.001). In DLD1 cell lines, LV-inhibitors group was higher in the expression of NFIB protein than LV-INC group (p < 0.001). f In HCT116 cell lines, LV-mimics group was lower in the expression of NFIB mRNA than LV-mNC group (p < 0.001). In DLD1 cell lines, LV-inhibitors group was higher in the expression of NFIB mRNA than LV-INC group (p < 0.001). g The wild-type and mutant plasmids of NFIB mRNA 3 UTR were constructed on the potential binding sites of miR-138-5p and NFIB mRNA. h Double luciferase assay verified that miR-138-5p banded with wild type NFIB mRNA 3 UTR instead of mutant type (p < 0.001). i The NFIB siRNA with the best interference effect sequences was screened for subsequent experiments