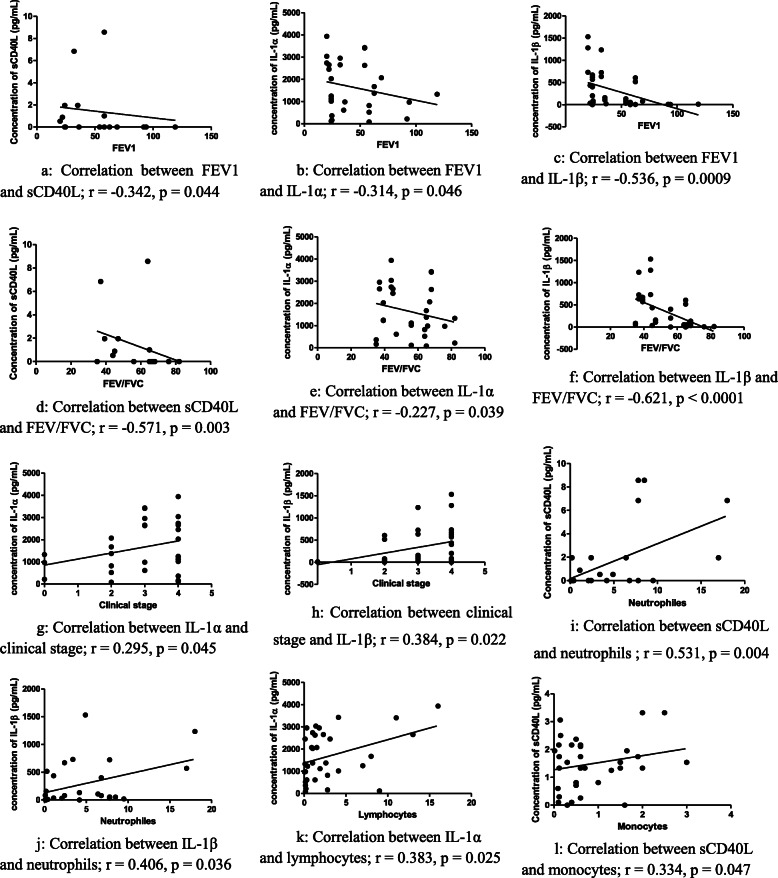
Fig. 2.
Significant correlations between cytokines and spirometric data or cells in the COPD patients with the history of smoking. a: Correlation between FEV1 and sCD40L; r = -0.342, p = 0.044. b: Correlation between FEV1 and IL-1α; r = -0.314, p = 0.046. c: Correlation between FEV1 and IL-1β; r = -0.536, p = 0.0009. d: Correlation between sCD40L and FEV/FVC; r = -0.571, p = 0.003. e: Correlation between IL-1α and FEV/FVC; r = -0.227, p = 0.039. f: Correlation between IL-1β and FEV/FVC; r = -0.621, p < 0.0001. g: Correlation between IL-1α and clinical stage; r = 0.295, p = 0.045. h: Correlation between clinical stage and IL-1β; r = 0.384, p = 0.022. i: Correlation between sCD40L and neutrophils ; r = 0.531, p = 0.004. j: Correlation between IL-1β and neutrophils; r = 0.406, p = 0.036. k: Correlation between IL-1α and lymphocytes; r = 0.383, p = 0.025. l: Correlation between sCD40L and monocytes; r = 0.334, p = 0.047. Legend: FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the first second. FVC: forced vital capacity. IL: interleukin. sCD40L: soluble cluster differentiation 40 ligand. r = Coefficient of correlation: - When r is positive, this means that the concentration of cytokine and the values of spirometric data (or the concentration of cells) vary in the same direction. - When r is negative, this means that the concentration of cytokine and the value of spirometric data (or concentration of cells) vary in the opposite direction. p = significance threshold: - If p is greater than 0.05, the correlation is not significantly different. - If p is less than or equal to 0.05, the correlation is statistically significant