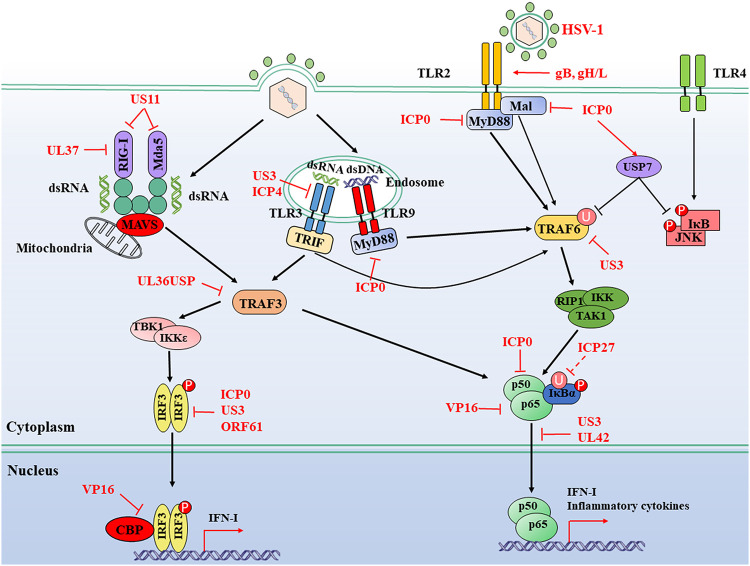
FIG 1.
HSV-1-mediated evasion of the RLR and TLR signaling pathway. TLRs are located at both the plasma membrane and endosomes. They sense different ligands like viral dsRNA, dsDNA, and glycoproteins; transduce signals through TRIF and MyD88; and then lead the activation of IRFs and NF-κB. RIG-I and MDA5 detect distinct RNA structures and signal through the adaptor protein MAVS protein to trigger IRF3 and NF-κB activation. The IFN-I and inflammatory cytokines are induced for antiviral immunity. HSV-1 proteins can hijack multiple steps downstream of RLR and TLR signaling pathways. Solid lines indicate confirmed interactions between adaptors and HSV-1 proteins. Dashed lines indicate uncertain interactions or that the underlying mechanism is unknown. CBP, CREB-binding protein; P, phosphate; U, ubiquitin.