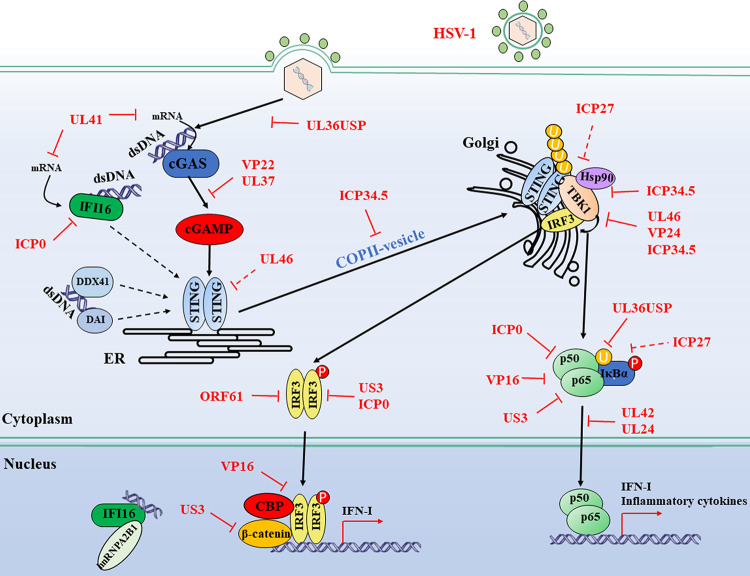
FIG 2.
Evasion of the DNA sensor-mediated IFN-I signaling pathway by HSV-1. Cytosolic DNA sensors, such as cGAS, IFI16, DDX41, and DAI, recognize double-stranded DNA in the cytosol and trigger IFN-I production through the transmission of a series of signals. Multiple steps in the DNA-sensing signaling pathway can be targeted by HSV-1 proteins, including both DNA sensor-mediated viral recognition and subsequent signaling. Many adaptors and transcription factors further downstream in the DNA sensor-mediated signaling pathway, such as TBK1, IRF3, p65, and p50, are shared by the RLR-mediated IFN-I signaling pathway. Therefore, it is plausible to consider that viral proteins targeting these molecules in the RLR-mediated signaling pathway may inhibit cytosolic DNA-sensing signals through a similar mechanism. Solid lines indicate confirmed interactions between adaptors and HSV-1 proteins. Dashed lines indicate uncertain interactions or that the underlying mechanism is not known. CBP, CREB-binding protein; P, phosphate; U, ubiquitin. (Based on data from reference 92.)