Fig. 1.
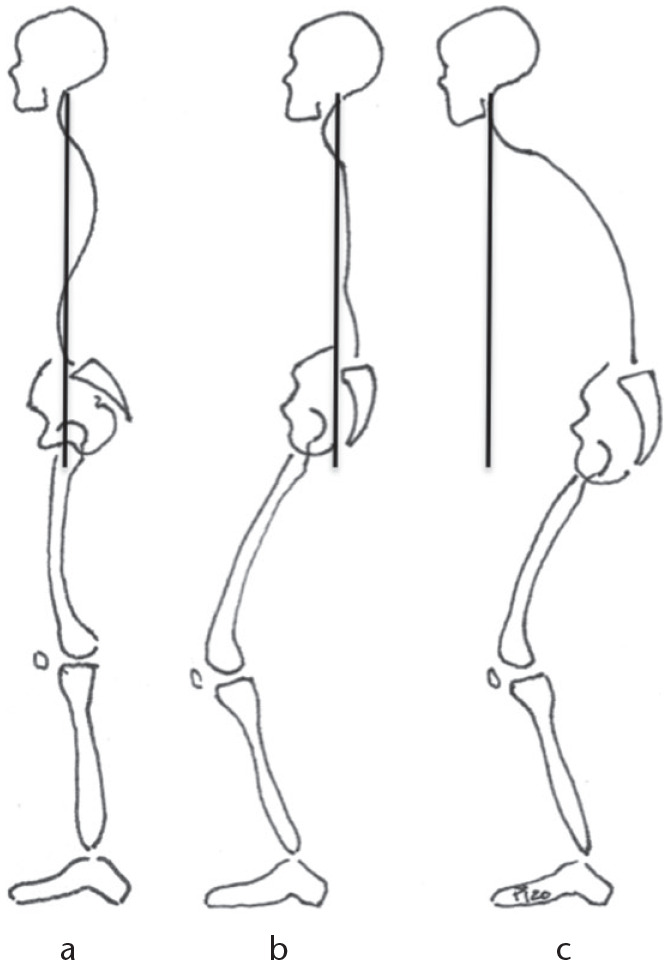
(A) Alignment is the correct positioning of the spinal curves when maintaining the head over the pelvis. (B) Malaligned but balanced due to compensation: cervical hyperlordosis, thoracic hypokyphosis, pelvic retroversion, hip extension, knee/ankle flexion, and posterior trunk shift. (C) Malaligned and unbalanced: compensation mechanisms are exhausted; malalignment appears shifting the gravity line forward, and pushing the body anteriorly.
