Figure 3.
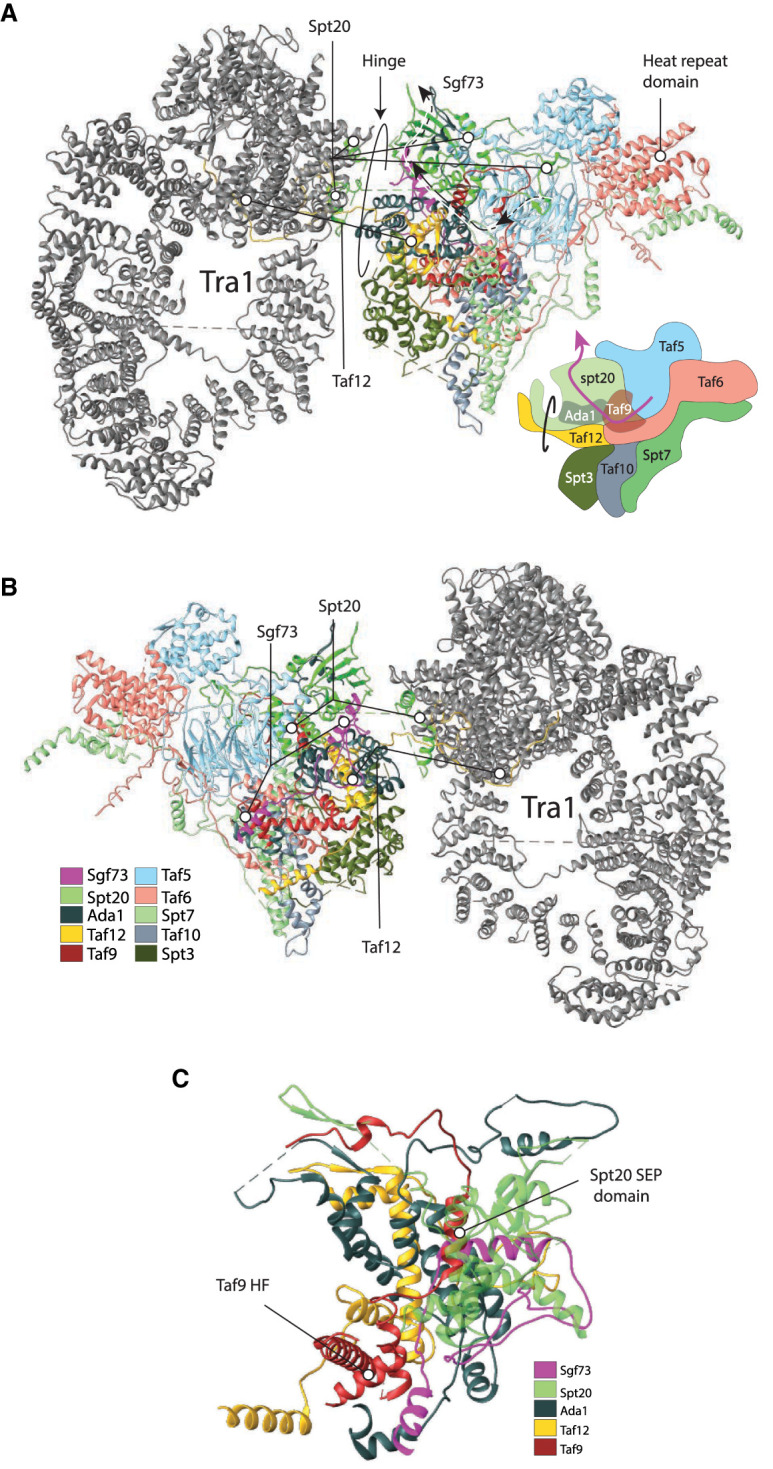
Anchor points for the enzymatic modules of the SAGA complex (A) Front view. PDB ID 6T9I and stylized cartoon. (B) Back view. (C) Back view close-up showing the insertion of Sgf73. (PDB ID 6T9I) (Wang et al. 2020). The DUB module connects via the insertion the C-terminal part of Sgf73, which enters the core proximal to the Taf9 histone fold, traverses an elongated domain of Ada1, and exits next to the Spt20 SEP domain (Papai et al. 2020; Wang et al. 2020). Spt20 is critical for the association of the DUB module. The HAT module docks to SAGA at subunit Taf6, where two helical domains—attributable to Ada3—lie at the surface of the Taf6 HEAT repeat domain. Taf5, Ta6, and Taf9 likely stabilize the configuration of Taf6 as well as the overall structure of the core module. The conformations of the enzymatic modules are dynamic in vivo, and this mobility allows the modifications on a stretch of nucleosomal histone tails up along the promoter region.
