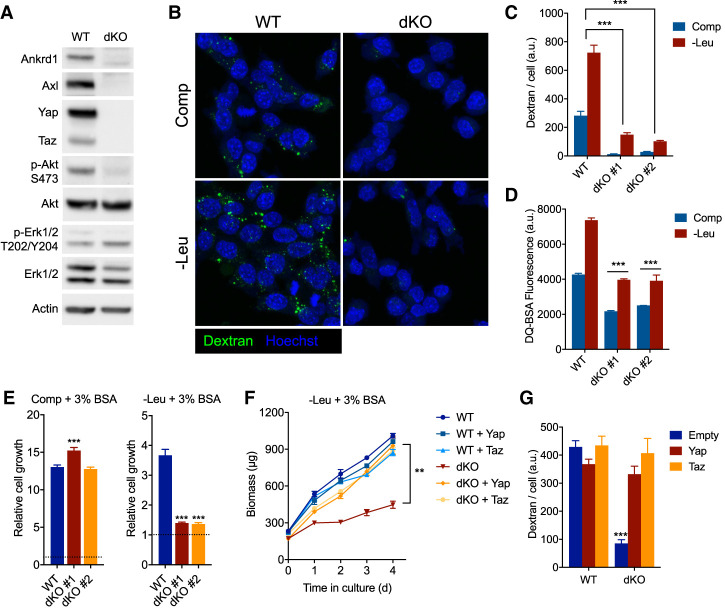
Figure 3.
Yap/Taz are essential for macropinocytosis and cell growth that is dependent on the catabolism of extracellular proteins. (A) Immunoblot of whole-cell lysates from Yap/Taz-deficient (dKO) or wild-type (WT) KRPC cells. (B) Confocal micrographs showing uptake of fluorescent dextran (green) and nuclei (Hoechst, blue) in Yap/Taz dKO or WT KRPC cells after 16 h of culture in complete (Comp) or leucine-free (−Leu) medium + 3% BSA. (C) Bar plot represents mean ± SEM dextran fluorescence intensity per cell, across 12 fields of view. (D) DQ-BSA fluorescence as measured by flow cytometry in Yap/Taz dKO and WT KRPC cells cultured for 24 h in complete or leucine-free medium + 3% BSA. DQ-BSA was added 4 h prior to analysis. Bars represent mean fluorescence intensity ± SD across three technical replicates. (E) Growth of Yap/Taz dKO or WT KRPC clones in complete (48 h) or leucine-free medium (96 h) + 3% BSA. (F) Growth of Yap/Taz dKO or WT KRPC cells transduced with retroviruses expressing a doxycycline-inducible Yap or Taz cDNA or empty vector in leucine-free medium + 3% BSA with 100 ng/mL doxycycline. (G) Dextran uptake in Yap/Taz dKO or WT KRPC transduced with retroviruses as in F, after culture for 16 h in leucine-free medium with 3% BSA and 100 ng/mL doxycycline. Bars represent mean fluorescence intensity per cell ±SEM across 12 fields of view. (***) P < 0.0001, (**) P < 0.005, one-way ANOVA, for C–G.