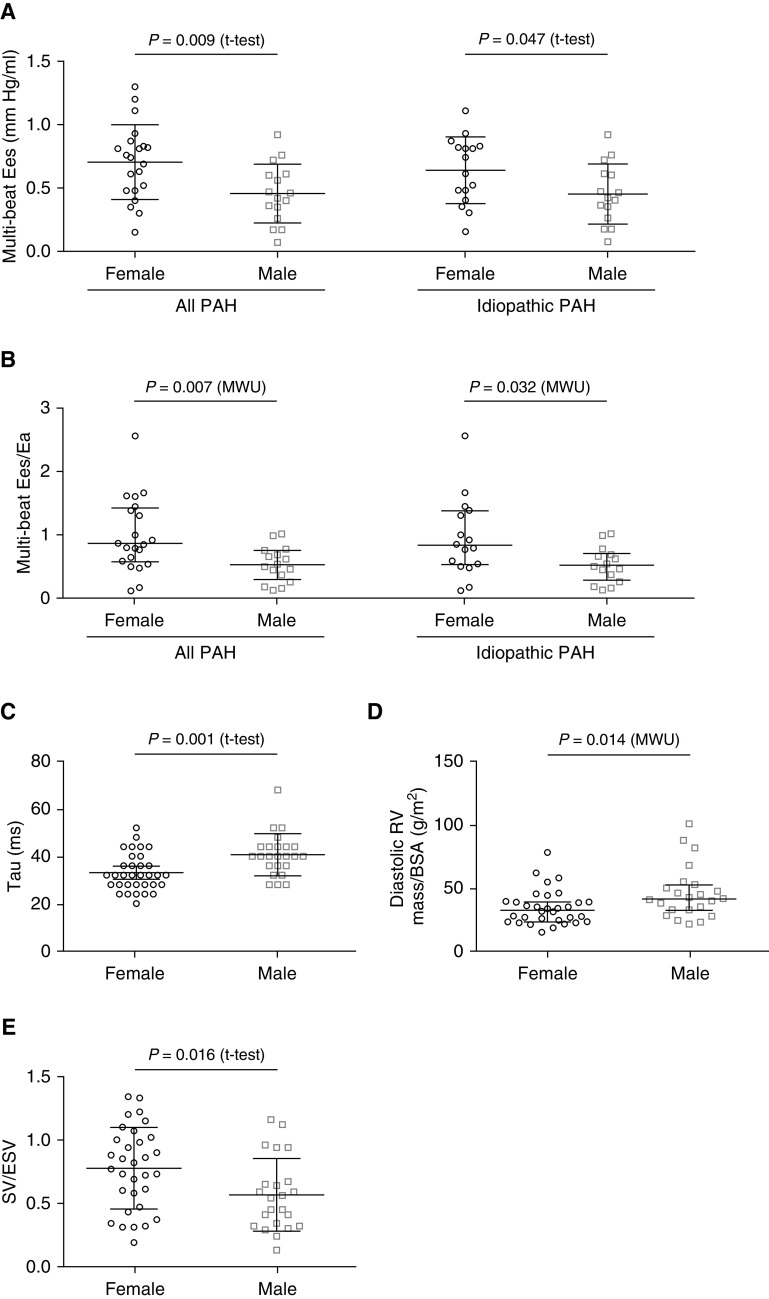
Figure 1.
Sex stratification of pressure–volume loop parameters and cardiac magnetic resonance–derived RV mass index and SV/ESV in patients with PAH. Compared with male patients, female patients had significantly improved (A) RV contractility (multibeat Ees; all PAH, n = 37; idiopathic PAH, n = 31), (B) RV–pulmonary arterial coupling (multibeat Ees/Ea; all PAH, n = 37; idiopathic PAH, n = 31), (C) early diastolic relaxation (Tau; all PAH, n = 57), (D) RV mass index (all PAH, n = 55), and (E) SV/ESV (all PAH, n = 55). Data are presented as (A, C, and E) means and SD for normally distributed variables or (B and D) medians and interquartile ranges for nonnormally distributed variables. Between-group differences were analyzed by Student’s t tests or Mann-Whitney U tests (SPSS, version 25.0; IBM). BSA = body surface area; Ea = arterial elastance; Ees = end-systolic elastance; ESV = end-systolic volume; MWU = Mann-Whitney U test; PAH = pulmonary arterial hypertension; RV = right ventricular; SV = stroke volume.