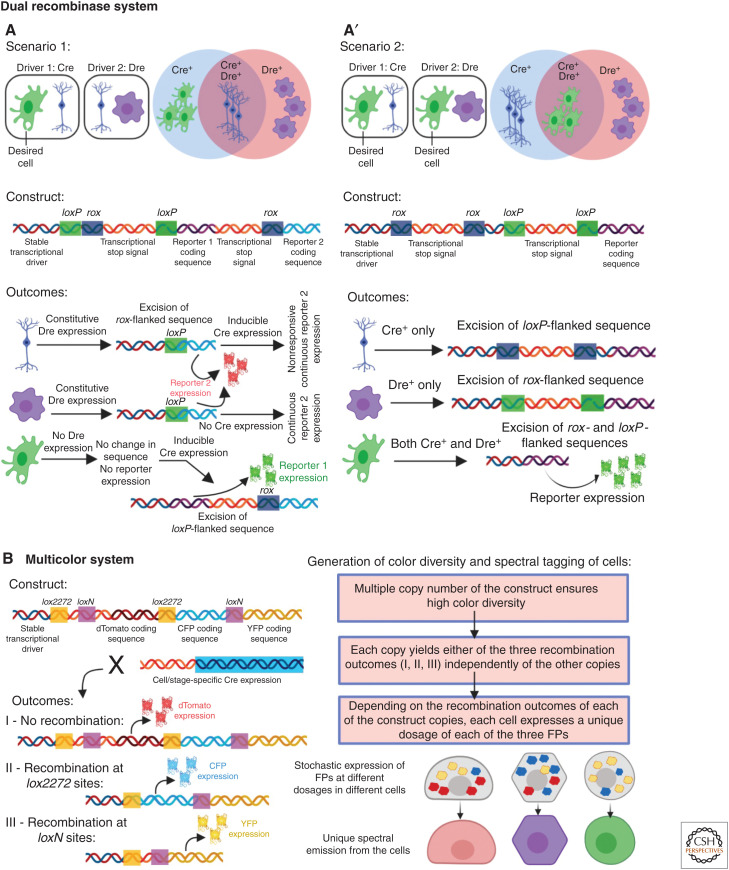
Figure 2.
Different applications of site-specific recombination systems for precise lineage tracing. (A,A′) The dual recombination system uses Cre-lox and Dre-rox recombination systems together to increase the precision of lineage tracing by resolving the issues of promiscuous Cre expression. (A) In some studies (scenario 1), promiscuous expression of Cre is abolished by Dre-rox-mediated excision of a specific reporter gene (reporter 1) from the nonspecific cell types. Cells that express only Dre (violet) or both Dre and Cre (blue) can only express reporter 2 (red). The desired cell only expresses Cre and thus the Cre-lox-mediated recombination allows it to express reporter 1 (green). (A′) In certain cases (scenario 2), combinatorial expression of both Cre and Dre is required for the reported gene expression, restricting the reporter expression only in the overlapping cells. Cells that express only Cre (blue) or Dre (violet) cannot express the reporter, but combinatorial recombination in the desired cell (green) allows the expression of the reporter. (B) The multicolor system depends on stochastic and combinatorial expression of different fluorescent proteins (FPs) that allow unique spectral emission from different cells and, thus, uniquely labeling them. The construct allows expression of dTomato (outcome I) without any recombination. Cre mediates recombination either between the lox2272 or the loxN sites, resulting in the expression of CFP (outcome II) or YFP (outcome III). By inheriting multiple copies of the construct, and different outcomes from each copy, each cell independently acquires a unique combination of the FPs, resulting in unique spectral emission.