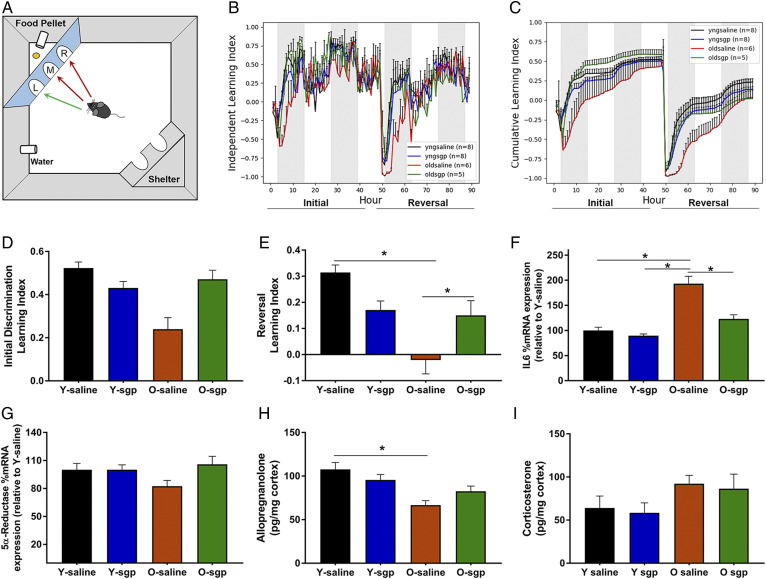
Fig. 6.
The effects of IL-6 inhibition on neurosteroid synthesis and working memory. A: Illustration of the PhenoTyper home cage system containing the cognition wall used to assess working memory. On days 1–2, the initial learning period, the mouse must learn to enter the left most entry of the cognition wall at least five times to receive a food pellet. On days 3–4, the reversal period, the mouse learns to enter the right most entry at least five times to receive a food pellet. B, C: Working memory assessment in young and old mice following a 2 week intracerebroventricular infusion of either saline or sgp130 (IL-6 inhibitor) to the lateral ventricle of the brain. Learning indices are calculated by (correct entries – incorrect entries)/total entries made per hour. B: The independent index represents the average learning index per group across each hour of the initial learning and reversal periods. C: The cumulative index represents the average learning index per group accumulated over consecutive hours in both the initial learning period and the reversal period. D: Average learning indices per group during the initial discrimination period. E: Average learning indices per group during the reversal period (n = 5–8 per group, two-way ANOVA, Tukey HSD pairwise comparisons, *P < 0.05). F–I: Cerebral cortex tissues from young and old mice treated with saline or the IL-6 inhibitor, sgp130 (n = 5–8 per group, two-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05). F: Percent mRNA expression of IL-6 across groups relative to young. G: Percent mRNA expression of 5α-reductase across groups relative to young. H, I: AlloP and CORT levels in the cortex following saline or sgp130 treatment. Statistics were adjusted for multiple comparisons. Only significant differences are depicted in the figure. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.