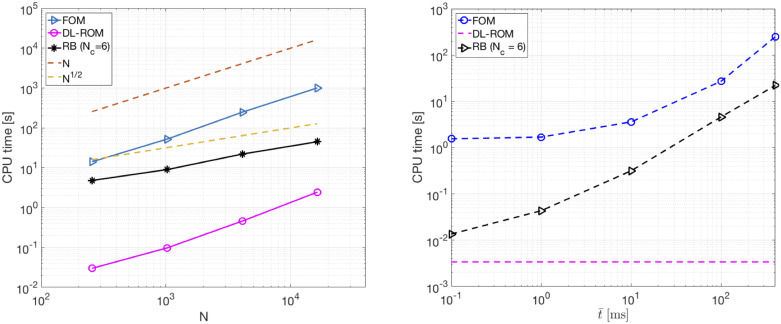
Fig 5. Test 1: FOM, DL-ROM and POD-Galerkin ROM CPU computational times.
Left: CPU time required to solve the FOM, by DL-ROM at testing time with n = 3 and by the POD-Galerkin ROM at testing time with Nc = 6 vs. N. The DL-ROM provides the smallest testing computational time for each N considered. Right: FOM, POD-Galerkin ROM and DL-ROM CPU computational times to compute vs. averaged over the testing set. Thanks to the fact that the DL-ROM can be queried at any time istance it is extremely efficient in computing with respect to both the FOM and the POD-Galerkin ROM.