Figure 2.
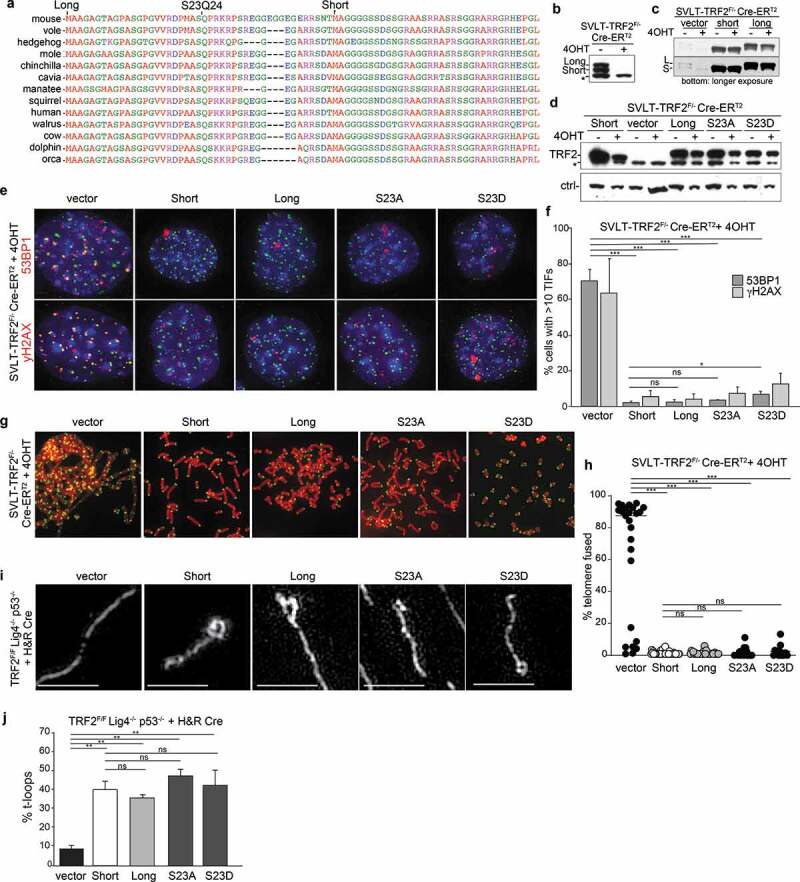
Two isoforms of TRF2 are equally proficient in telomere protection and t-loop formation. (a) Sequence alignment showing the conservation of the N-terminal sequence of TRF2. The two ATGs giving rise to the short and long form of TRF2 are indicated as well as the SQ site. Sequences were aligned using Multalign. (b) Immunoblot showing two isoforms of TRF2 that are removed upon Cre treatment of TRF2F/F MEFs. (c) Immunoblot for TRF2 in the indicated MEFs with and without Cre treatment expressing the Long and Short versions of TRF2 as well as the S23A and S23D mutants of the Long form. (d) TIF assay using 53BP1 or γ-H2AX IF for detection of the telomere damage response on cells as in (c). (e) Quantification of the TIF response detected as in (d). Averages and SDs from three independent experiments with 50 nuclei each. Significance as above in Figure 1. (f) Examples of metaphase spreads with telomeres detected by FISH using the indicated MEFs infected as in (c) and treated with Cre (96 h). (g) Quantification of telomere fusions detected as in (f). Scoring was performed in three independent experiments with 10 metaphase per experiment. Averages, SDs, and significance as in Figure 1. (h) Examples of the structure of telomeric DNA detected in the indicated MEFs expressing the indicated forms of TRF2 and treated with Cre (120 h). Scale bars: 2.5 μm. (i) Quantification of t-loop frequencies detected as in (h). Averages and SDs from three independent experiments (>100 molecules scored each). Significance determined using a two-tailed unpaired t-test (n.s. not significant; ** p < 0.01).
