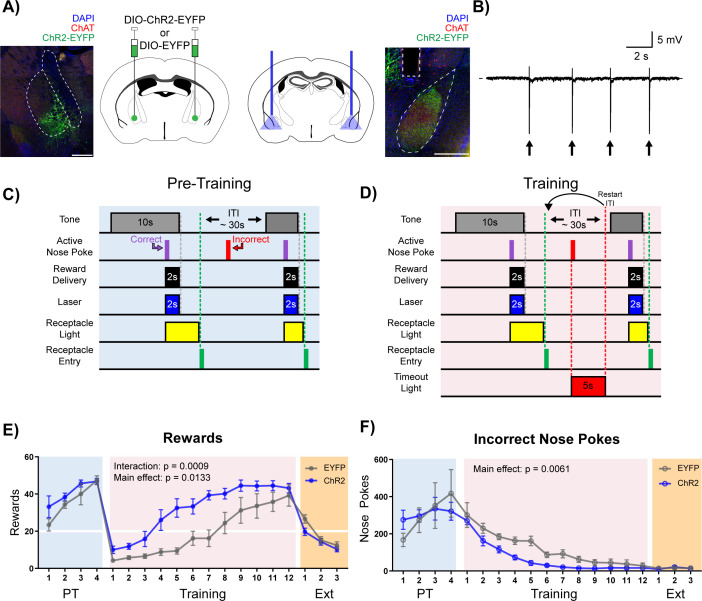
Figure 4. Stimulation of cholinergic terminal fibers in the BLA enhances cue-reward learning.
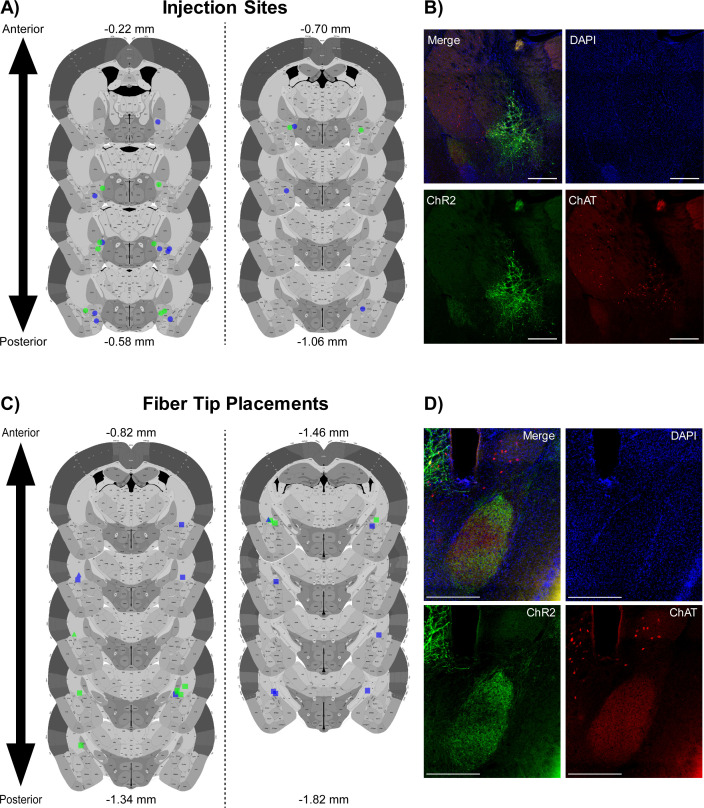
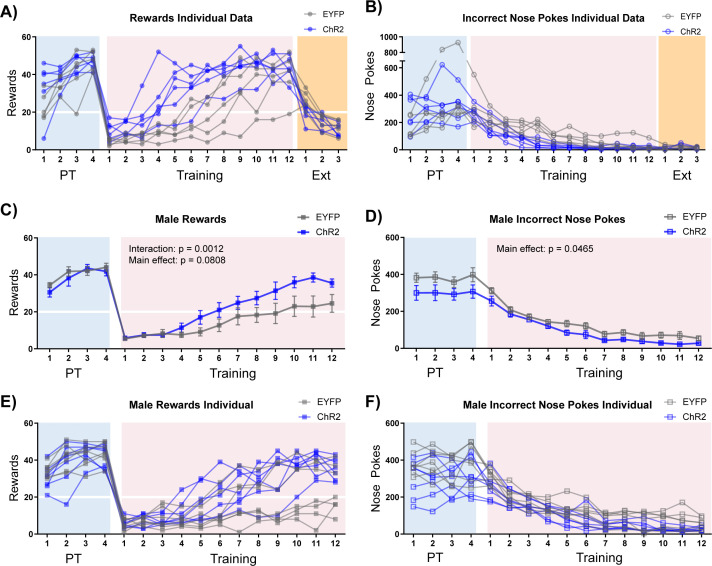
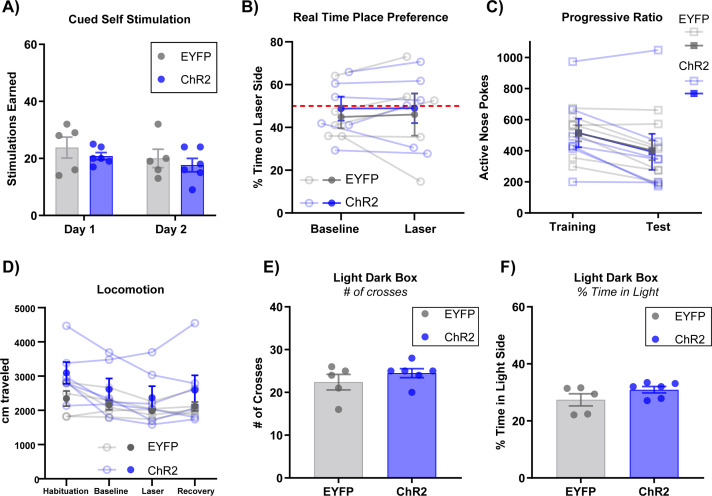
(A) Schematic of optical stimulation of ChAT+ terminal fibers projecting to the BLA. Left: Bilateral AAV injection into the NBM of ChAT-IRES-Cre mice to gain optical control over ChAT+ NBM cells and representative coronal brain slice showing ChR2-EYFP expression. White dashed lines: internal capsule and globus pallidus outlines. Blue: DAPI, red: ChAT, green: ChR2-EYFP. Scale: 500 µm, individual injection sites shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1A and separate channels shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1B. Right: Bilateral optical fiber implantation above BLA to stimulate BLA-projecting ChAT+ NBM cells. Representative coronal brain slice showing ChR2-EFYP expression and fiber tip placement. Gray dashed rectangle: fiber tract. White dashed: BLA outline. Blue: DAPI, red: ChAT, green: ChR2-EYFP. Scale: 500 µm, individual fiber tip placements shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1C and separate channels shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 1D. Injection sites and fiber tip placements for males from Figure 4—figure supplement 3C–F shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 4A–B. (B) Optical stimulation validation via local field potential recordings. Extracellular recording of action potentials induced by optical stimulation of ChAT+ NBM cells expressing ChR2. Arrows indicate 60 ms laser pulse. (C–D) Details of the Cue-Reward Learning Paradigm (C) During Pre-Training, auditory tones were presented on a variable interval 30 schedule (VI30), during which an active nose poke (correct) yielded Ensure reward delivery and 2 s of optical stimulation but there was no consequence for incorrect nose pokes (active nose pokes not during tone). (D) Training was identical to Pre-Training, except incorrect nose pokes resulted in a 5 s timeout, signaled by house light illumination, followed by a restarting of the ITI. (E) Behavioral performance in a cue-reward learning task improves with optical stimulation of ChAT+ fibers in BLA. EYFP- and ChR2-expressing mice earn similar numbers of rewards during PT (blue shaded region). ChR2-expressing mice more rapidly earn significantly more rewards than EYFP-expressing mice during Training (pink shaded region). No significant differences were observed during extinction training (orange shaded region). Horizontal white line: acquisition threshold, when a mouse began to earn ~20 rewards consistently in Training. Mean ± SEM, EYFP: n = 5, ChR2: n = 6. Individual data are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3A. Data for males shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3C,E. (F) EYFP- and ChR2-expressing mice made similar numbers of incorrect nose pokes during Pre-Training. ChR2-epxressing mice made significantly fewer incorrect nose pokes than EYFP-expressing mice in Training. No significant differences were observed during extinction training. Mean ± SEM, EYFP: n = 5, ChR2: n = 6. Individual data are shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3B. Data for males shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 3D,F. Additional behavioral assays shown in Figure 4—figure supplement 5A–F.
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Injection sites and optical fiber placements.
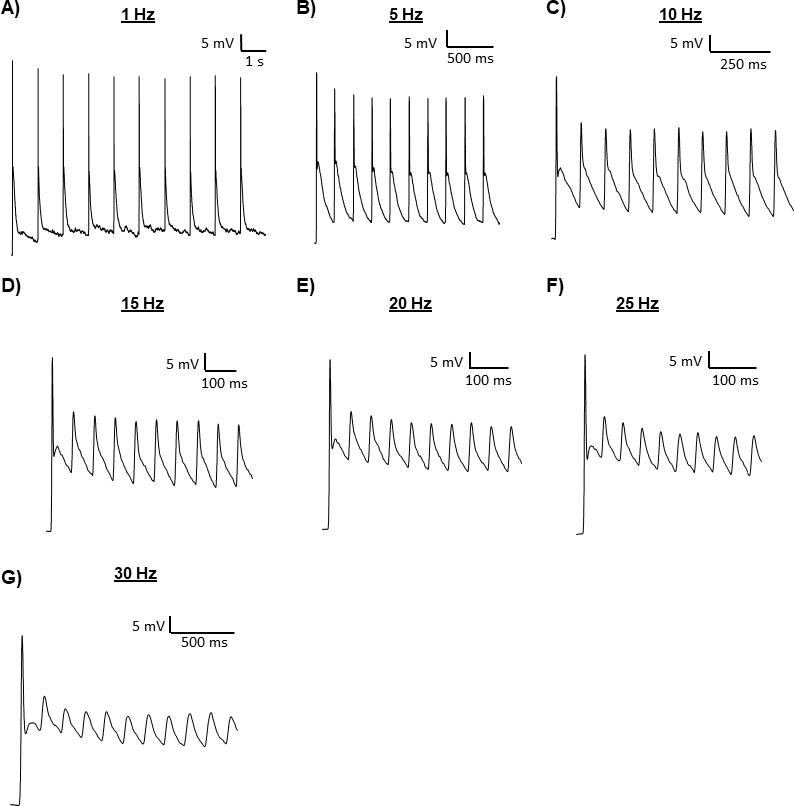
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Ex vivo electrophysiology.