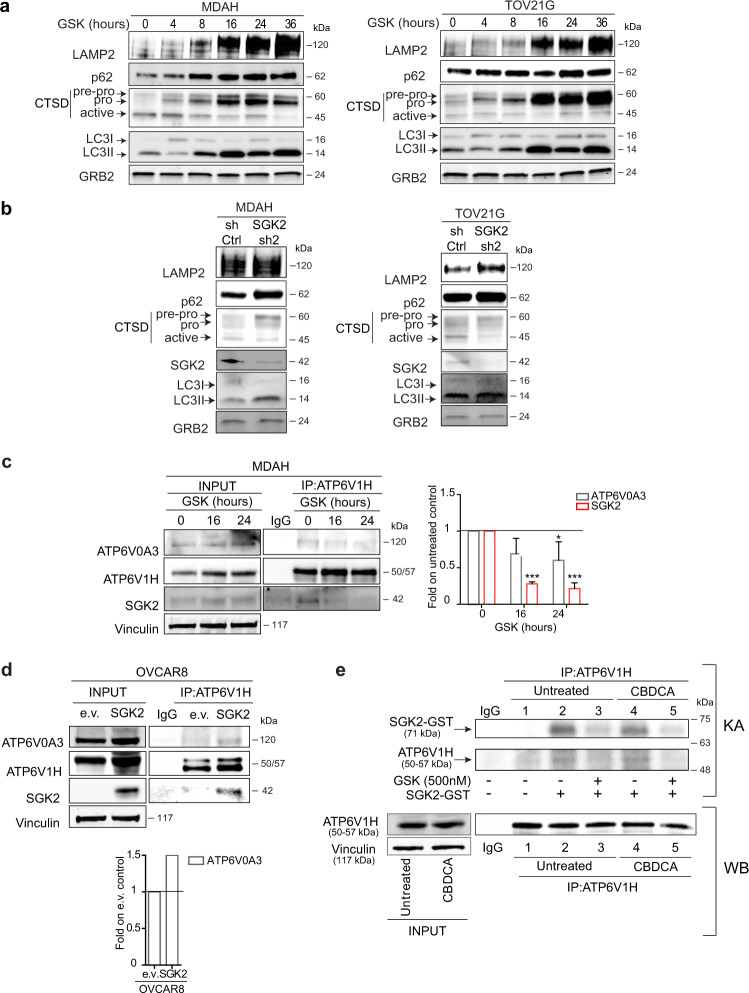
Fig. 7. SGK2 inhibition causes autophagy blockade altering activation of lysosomal cathepsins.
WB analyses of LAMP2, p62, Cathepsin D (CTSD) and LC3I/LC3II in cell lysates from MDAH and TOV21G cells treated with GSK650394 35 μM (GSK) for the indicated time a or silenced for SGK2 expression b. GRB2 was used as loading control. c Co-immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis of endogenous ATP6V1H with SGK2 and ATP6V0A3 in MDAH cells untreated or treated with GSK650394 35 μM (GSK) for 16 and 24 h. Cell lysates immunoprecipitated with ATP6V1H were probed for the expression of ATP6V1H, SGK2, and ATP6V0A3. The expression of the three proteins in the corresponding lysates (INPUT) is reported on the left. The right graph shows the quantification of SGK2 and ATP6V0A3 bound to ATP6V1H in GSK treated cells expressed as fold respect to untreated cells and represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance was calculated using two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. d Co-immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis of endogenous ATP6V1H with SGK2 and ATP6V0A3 in OVCAR8 cells stably overexpressing SGK2. Cell lysates immunoprecipitated with ATP6V1H were probed for the expression of ATP6V1H, SGK2 and ATP6V0A3. The expression of the three proteins in the corresponding lysates (INPUT) is reported. The lower graph shows the quantification of ATP6V0A3 bound to ATP6V1H in SGK2 overexpressing cells expressed as fold respect to cells transfected with the empty vector (e.v.). e In vitro kinase assay (upper panel) using SGK2 active recombinant protein incubated with endogenous ATP6V1H immunoprecipitated from untreated and CBDCA-treated MDAH cells (500 μg/ml 16 h) (lower panel). Western blot analyses of 1/10 of the immunoprecipitated ATP6V1H protein used in each line (1–5) and the corresponding lysates (INPUT) are reported (lower panel). Vinculin was used as loading control in c–e. IgG indicates a lysate IP with unrelated antibody. (See also Fig. S8).