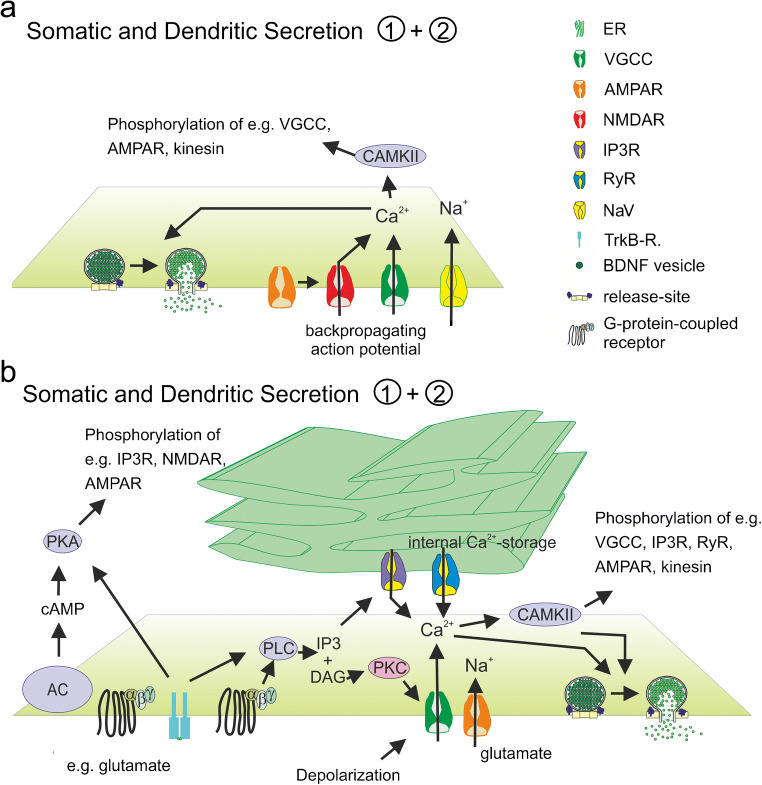
Fig. 2.
Suggested mechanisms for somatic and dendritic release of BDNF. BDNF release is dependent on extracellular Ca2+-influx (a) and/or intracellular Ca2+-release from internal stores (ER) Ca2+-influx (b). Ca2+-influx from extracellular space is mediated via VGCC and/or NMDAR (a, b). Ca2+ release from ER is mediated via IP3R or RyR (b). Increased burst firing activity, glutamate, or other ligands of GPCR mediate transient intracellular Ca2+-increase important for vesicle exocytosis. AC adenylate cyclase, CAMKII calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; DAG diacylglycerol, ER endoplasmatic reticulum, IP3 inositol triphosphate, IP3R inositol-3-phosphate receptor, NaV voltage-gated sodium channel, NMDAR N-methyl d-aspartate receptor, PKA protein kinase A, PKC protein kinase C; PLC phospholipase C; RyR ryanodine, VGCC voltage-gated calcium channel. Adapted from Brigadski and Leßmann, Neuroforum, 2014