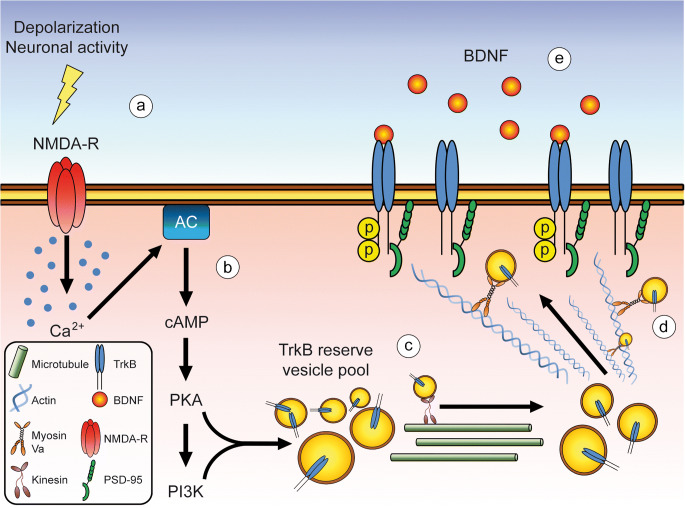
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of cAMP-mediated TrkB surface translocation via PKA/PI3K. Neuronal activity triggers Ca2+ entry via AMPA and NMDA receptors (a). Ca2+ stimulates adenylyl cyclase activity followed by elevation of cAMP levels which trigger PKA and PI3K activity (b). Rapidly available intracellular reserve pools of TrkB are mobilized in a microtubule-dependent manner (c). TrkB containing vesicles are transported to distinct target sites at the cell surface, like dendritic spines where they integrate. In the dendritic target area, TrkB is transported via Myosin Va in an actin-dependent manner and associates with PSD-95 which promotes guided transport and integration into the PSD (d). At the cell surface, TrkB is sensitive for BDNF binding which activates TrkB via phosphorylation at C-terminal tyrosine residues (e)