Figure 2:
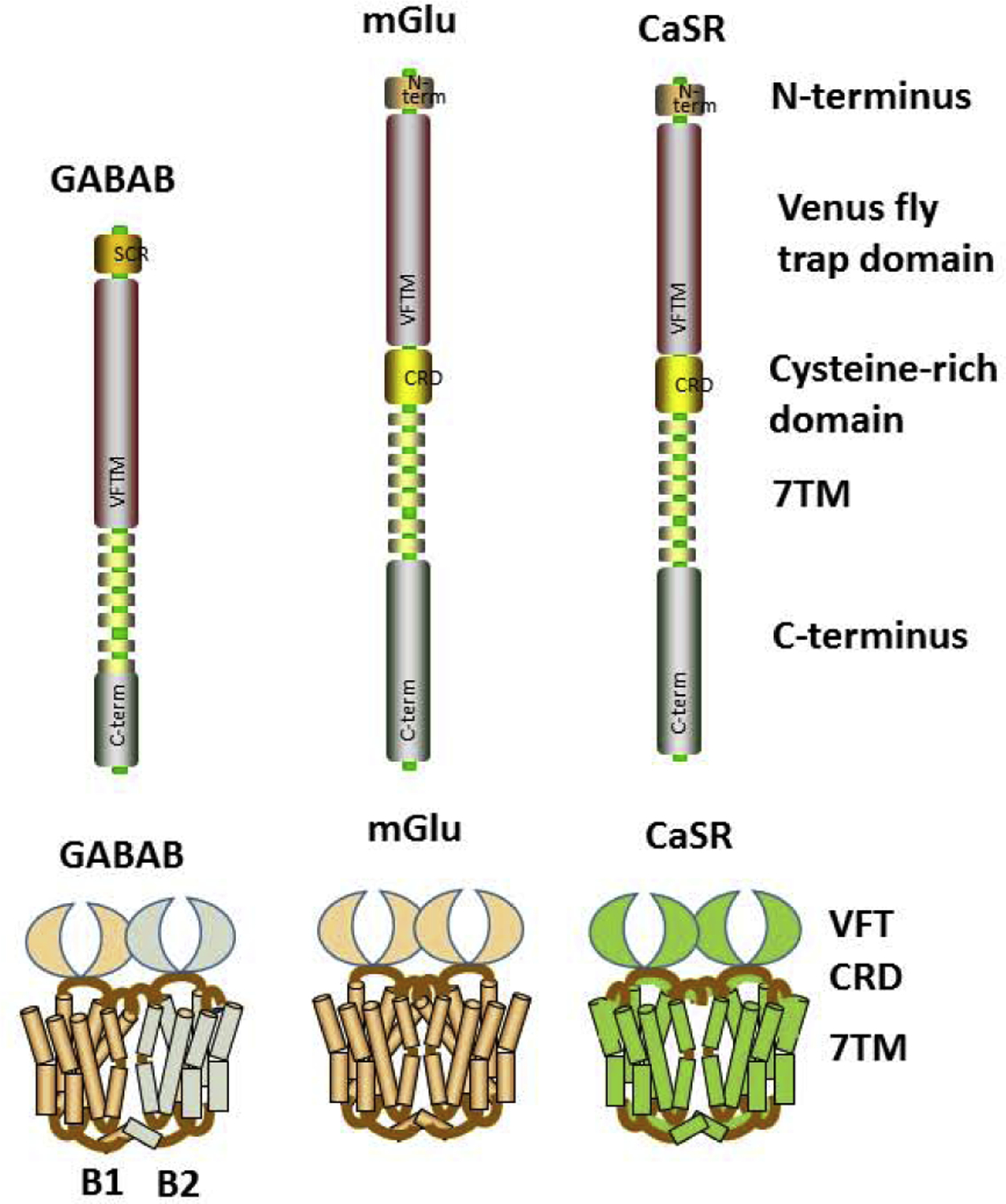
Class C GPCR Structures. Differing substantially from other GPCR classes, members of the Class C GPCR share a unique structure composed of a very large extracellular domain and the ability to form constitutive dimers, with both homo- and heterodimerization depending on the members, and being obligatory for functionality. A unique extracellular aspect is the Venus flytrap (VFT) domain and highly conserved nine-cysteine residue rich domain (CRD; except for GABABR that lack CRD).
