Extended Data Figure 7. Analysis of putative endoproteolytic propeptide removal in AbLS.
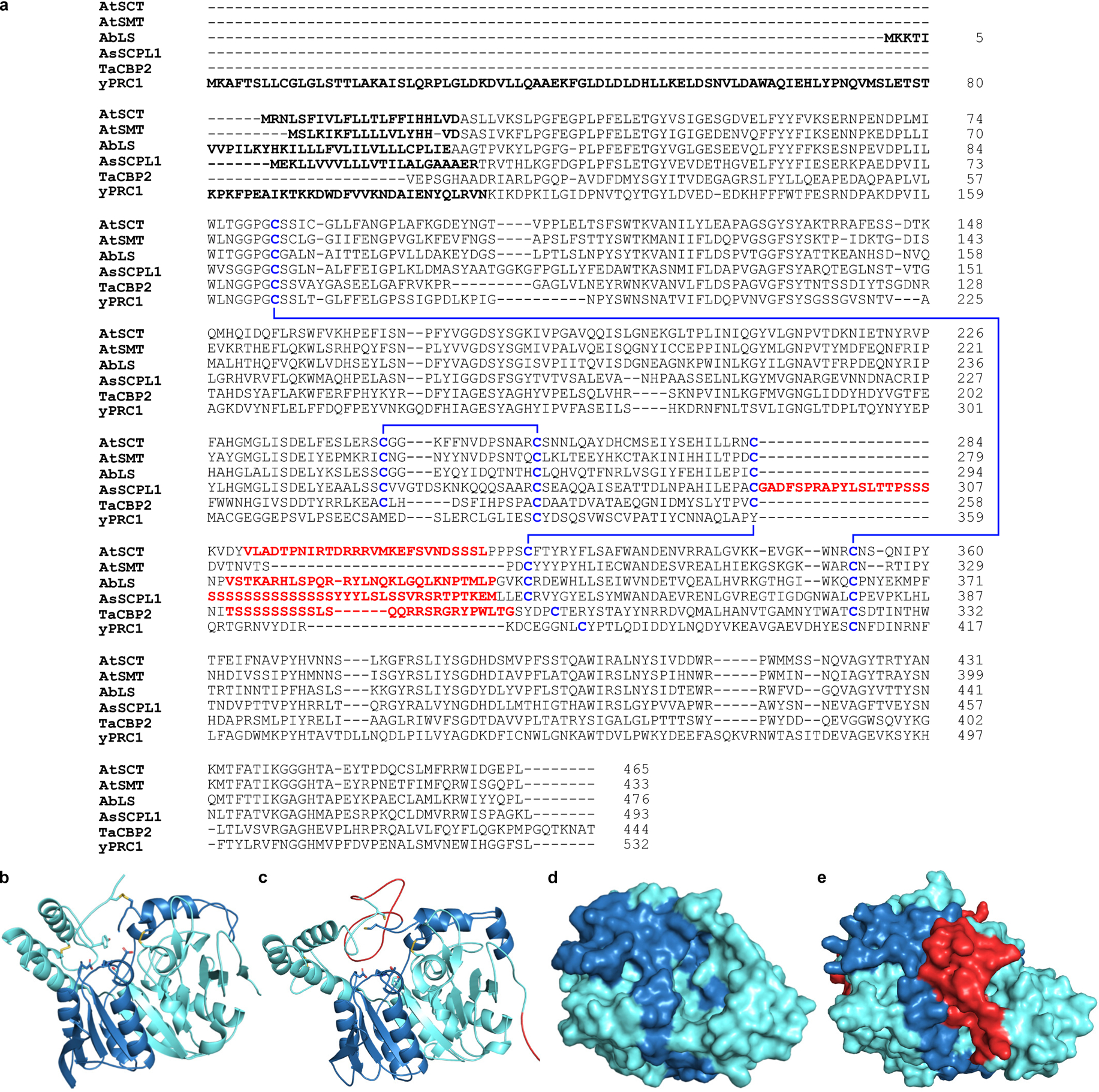
(a) Sequence alignment of AbLS with characterized serine carboxypeptidases and SCPL acyltransferases known to possess (AtSCT, AsSCPL1, TaCBP2) or lack (AtSMT, yPRC1) proteolytically-removed internal propeptide linkers (red). Putative N-terminal signal peptides are indicated in bold; disulfide bonds are indicated in blue. AtSCT, Arabidopsis thaliana sinapoylglucose: choline sinapoyltransferase; AtSMT, A. thaliana sinapoylglucose:malate sinapoyltransferase; AbLS, Atropa belladonna littorine synthase; AsSCPL1, Avena strigosa avenacin synthase; TaCBP2, Triticum aestivum carboxypeptidase 2; yPRC1, yeast carboxypeptidase Y. (b,d) Crystal structure of TaCBP2 (PDB: 1WHT) in (b) cartoon and (d) surface representation showing disulfide bonds (yellow) and internal propeptide removal sites. (c,e) Homology model of AbLS based on the crystal structure of TaCBP2 in (c) cartoon and (e) surface representation showing N-terminal signal peptide (red, bottom right in c), disulfide bonds (yellow), and putative internal propeptide (red, top/middle) which appears to block active site access. Note that surface views in d and e are rotated 90° toward the viewer.
