Fig. 6.
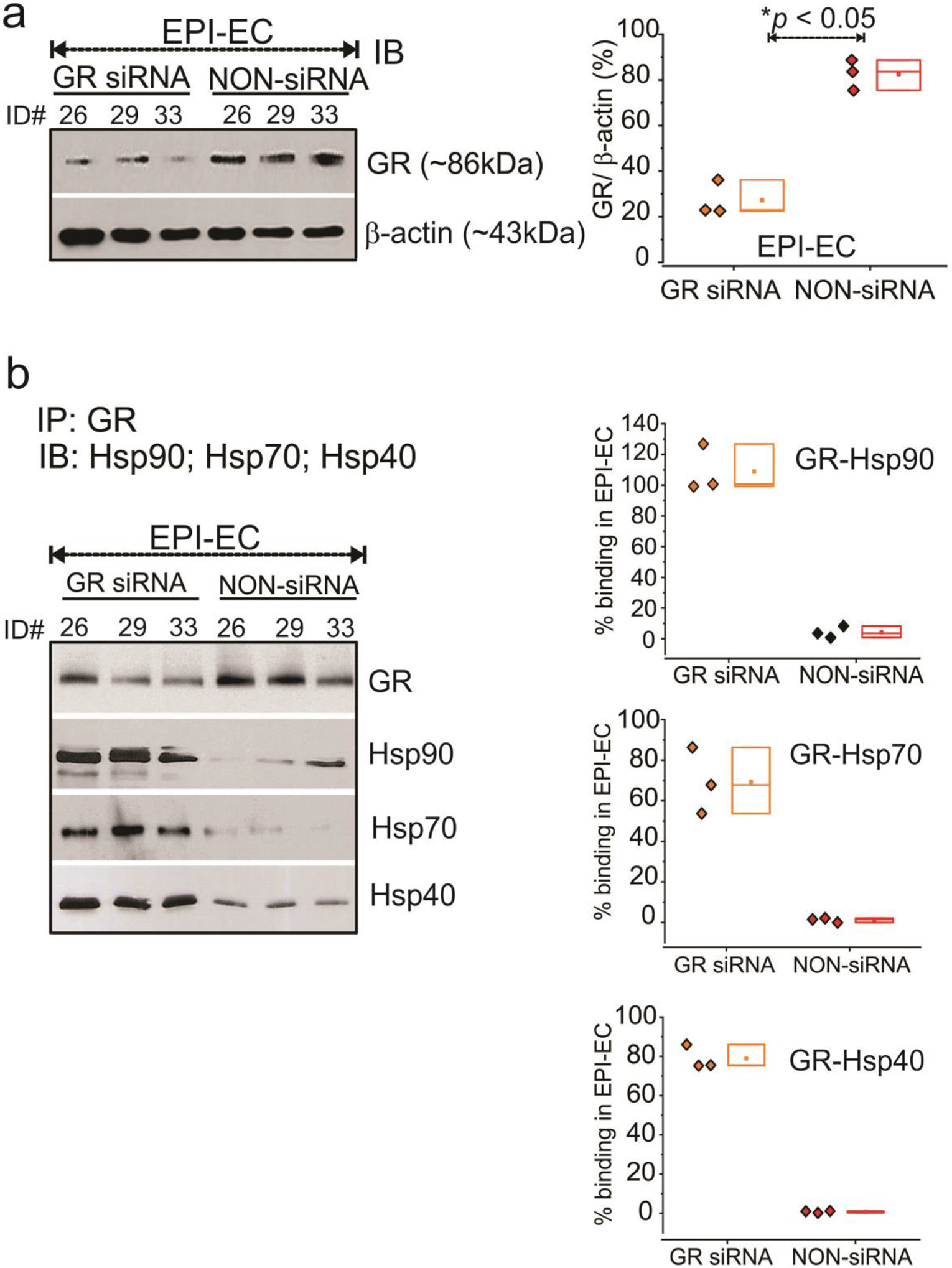
GR silencing in human EPI-ECs alters GR-Hsp interaction. (a) GR silencing of genes in EPI-ECs was evaluated by western blot and compared with non-siRNA EPI-ECs counterparts (n = 3 subjects #ID, 26, 29, 33). β-actin was used as a loading control and normalization. (b) The interaction of GR and Hsps were compared within the GR-silenced and non-silenced EPI-ECs by immunoprecipitation analysis and binding percentages were quantified. GR-siRNA on EPI-ECs showed higher trend of GR-Hsp90, GR-Hsp70 and GR-Hsp40 binding compared to non-siRNA EPI-ECs, suggesting that lowering GR levels can regulate GR-Hsp interactions and downregulates the GR maturation process in EPI-ECs. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM by ANOVA, *p < 0.05.
