Figure 2. Subgroup analyses of the effect of ARB use versus ACEI use on rehospitalization among older NH residents after myocardial infarction.
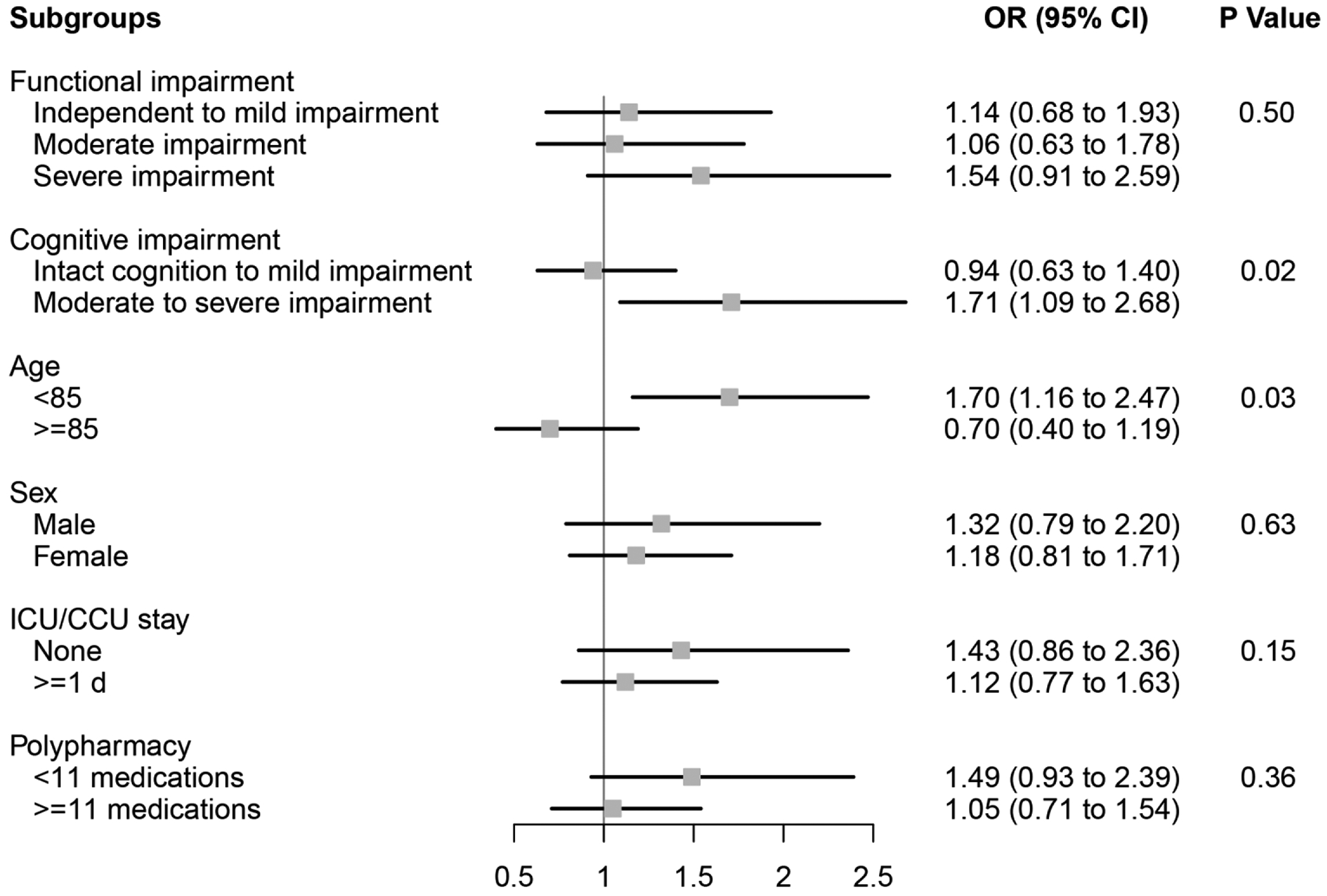
Functional impairment measured using the Minimum Data Set 28-point Activities of Daily Living (ADL) Scale; Independent to mild impairment is represented by an ADL score of 0 to 14 (independent to limited assistance required with ADLs), moderate impairment is represented by an ADL score of 15 to 19 (extensive assistance required with ADLs), and severe impairment is represented by an ADL score of ≥20 (extensive dependency in ADLs).
Cognitive impairment measured using the Minimum Data Set Cognitive Performance Score (CPS); Intact to Mild Impairment is represented by a CPS score of 0 to 2, and Moderate to Severe Impairment is a score of ≥3 (roughly equivalent to a Folstein Mini-Mental State Examination score of ≤14 of 30).
ACEI angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ARB angiotensin II receptor blocker, CCU coronary care unit, CI confidence interval, ICU intensive care unit, NH nursing home, OR odds ratio.
P Values for effect modification by subgroup characteristic.
