Figure 1.
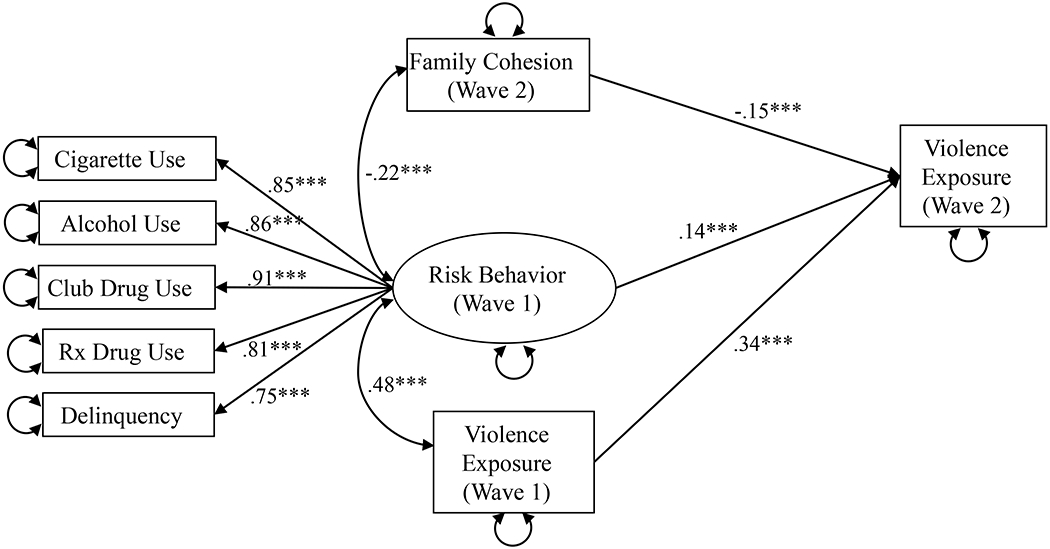
Structural regression model testing main effects among risk behavior, family cohesion, and victimization.
Note. *p < .05; **p < .01; ***p < .001. Standardized path coefficients displayed. Solid lines indicate significant paths. Dashed lines indicate nonsignificant paths. Covariates are not depicted; all primary variables were regressed on child age, gender, race/ethnicity, household income, parental education, urban vs. suburban vs. rural setting, and neighborhood safety.
