Figure 4. Effects of NPC-myricetin electrostatic interactions on NPC-hydroxyapatite binding.
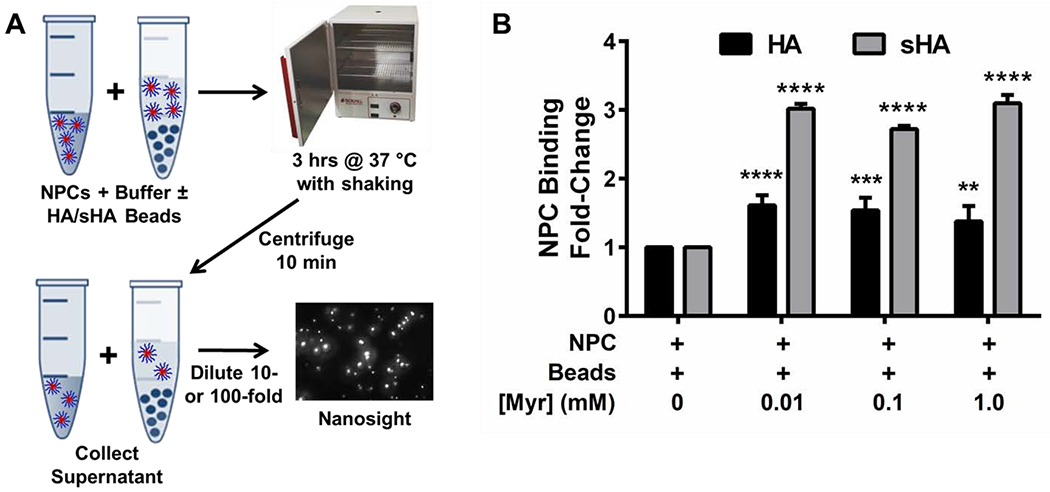
A) Schematic overview of NPC binding assay using hydroxyapatite (HA) and saliva-coated hydroxyapatite (sHA) beads and Nanosight particle count analysis. NPC solution and NPC + HA or NPC + sHA bead solution were incubated at 37 °C for three hours, centrifuged, diluted, and assessed via Nanosight analysis.B) Fold-change of NPC binding to HA (black bars) and sHA (grey bars) beads as a function of myricetin concentration, including unloaded NPCs and NPCs loaded with 0.01 mM, 0.1 mM, or 1.0 mM myricetin. Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments with each containing three replicates and five measurements per replicate, ns = no significant difference among groups, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, and **** p < 0.0001 from Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s correction for multiple comparisons compared to NPC + Beads controls without myricetin.
