Figure 1.
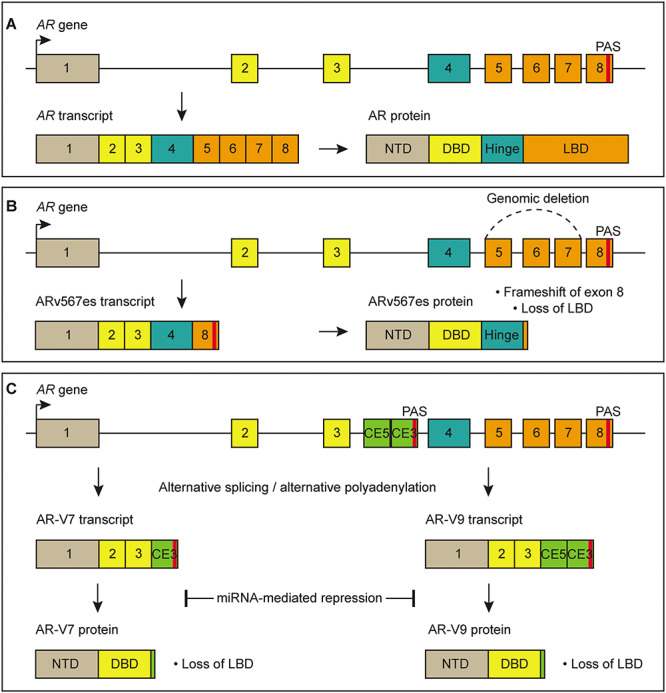
Genomic alterations and RNA-based mechanisms that regulate expression of AR and AR-Vs. (A) Canonical splicing of the AR gene to generate full-length AR mRNA and AR protein. (B) Example of a genomic alteration that causes expression of the AR-V ARv567es. Genomic deletion of exons 5 through 7 in the AR gene causes truncation of AR protein and loss of the LBD. (C) Examples of RNA-based mechanisms that regulate expression of AR-V7 and AR-V9. Alternative splicing and/or alternative polyadenylation can promote splicing of cryptic exons to generate mRNAs that encode truncated AR-Vs lacking the LBD. miRNAs can reduce stability or translation of AR-V mRNAs, causing reduced AR-V protein expression. NTD = N-terminal transcriptional domain, DBD = DNA-binding domain, LBD = C-terminal ligand-binding domain, CE5 = cryptic exon 5, CE3 = cryptic exon 3, PAS = polyadenylation site.
