Figure 1.
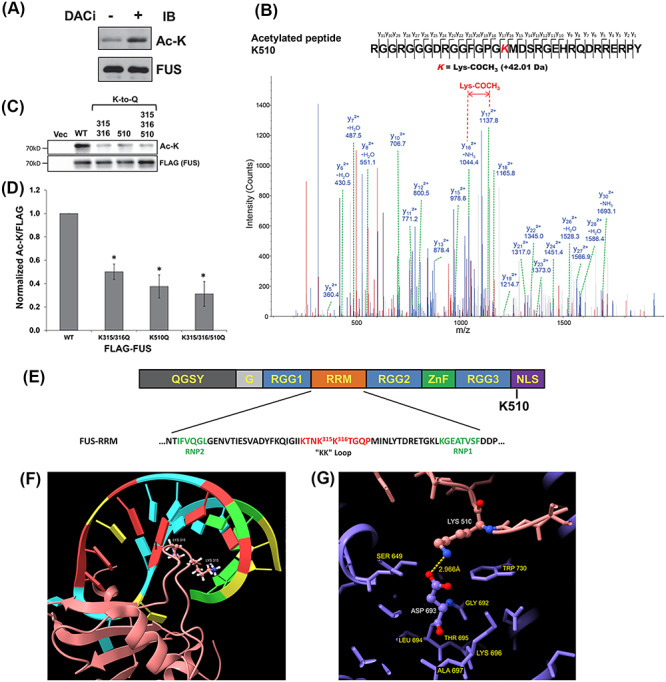
FUS is acetylated. (A) Endogenous FUS-IP from N2A cells treated with DACi cocktail (nicotinamide (30 mM), sodium butyrate (50 mM) and TSA (3 μM)) for 6 h. Immunoblotting was performed using the indicated antibodies. (B) Mass spectrometric identification of the acetylated FUS peptide RGGRGGGDRGGFGPGK510MDSRGEHRQDRRERPY. (C) 3× FLAG-tagged WT, K315Q/K316Q, K510Q, K315Q/K316Q/K510Q or FLAG vector control were transfected into HEK293T cells. After 24 h, cells were treated with DACi cocktail for 6 h, followed by FLAG-IP and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) Quantification of FUS acetylation from three independent experiments ±standard deviation (SD). Student’s t-test was performed for individual comparisons against WT (*P ≤ 0.05). (E) The domain structure of FUS showing the RRM domain sequence and acetylation sites. (F) NMR solution structure of FUS RRM domain (pink) showing K315 and K316 in the KK-loop bound to stem–loop RNA (protein data bank entry 6GBM). (G) Crystal structure of TNPO1/FUS-NLS (protein data bank entry 4FQ3) illustrating the FUS-NLS domain (pink) K510 adjacent to TNPO1 (purple) D693. Molecular graphics of FUS RRM and NLS domains visualized using UCSF ChimeraX (79).
