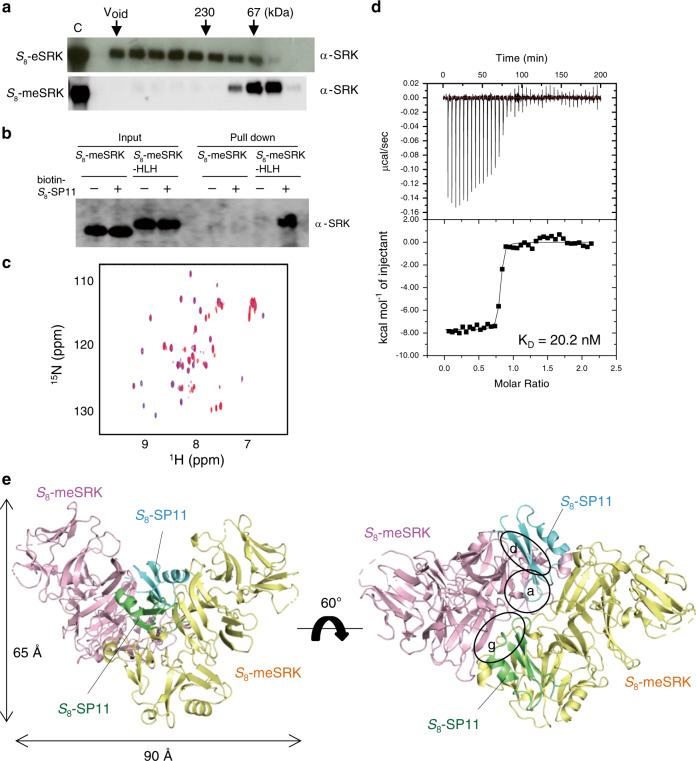
Fig. 1. Structure determination of S8-meSRK–S8-SP11 complex.
a Eleven amino acid mutations of S8-eSRK (S8-meSRK) suppress self-aggregation. The immunoblots show the fractions from size exclusion chromatography of S8-eSRK and S8-meSRK ectodomains expressed in insect cells. Arrows show the elution positions of molecular mass markers. C, control supernatants of insect cell culture expressing the recombinant proteins. b S8-meSRK possesses S8-SP11 recognition activity. The panel shows immunoblot analysis of pull-down eluates using biotin-S8-SP11 and insect culture media expressing S8-meSRK or S8-meSRK-HLH, which is an artificial fusion with the dimerization domain of a bHLH-ZIP protein18. c Chemical shift perturbation analysis of S8-SP11. Overlay of the spectrum of 15N-labeled S8-SP11 (blue) with that of 15N-labeled S8-SP11 co-existing with unlabeled S8-meSRK (red). d ITC analysis of the S8-meSRK–S8-SP11 interaction. Upper panel, thermogram; lower panel, integrated titration curve. e Overall structure of S8-meSRK–S8-SP11 heterotetramer. Two S8-meSRK (pink and yellow) and two S8-SP11 (cyan and green) molecules are shown as cartoon models. Dotted lines indicate disordered regions. Details of the labeled circles are shown in Fig. 2a, d, g.