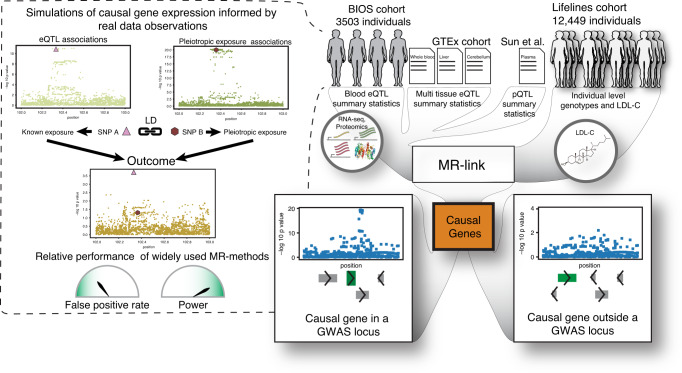
Fig. 1. Graphical representation of the study.
The Biobank Integrative Omics Study (BIOS) cohort was used to identify expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) and characterize the genetic architecture of gene expression. Dashed outbox: Knowledge used in a simulation scheme that mimicked gene-expression traits, including linkage disequilibrium (LD) between eQTL single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs). We used this simulation to assess the false positive rates and power for widely used Mendelian randomization (MR) methods. We applied our MR method, MR-link, to both the simulations and to individual-level data of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in 12,449 individuals (Lifelines) combined with BIOS and GTEx eQTL as well as protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL) summary statistics to identify gene-expression changes and protein level changes that are causally linked to LDL-C within or outside a genome-wide association study (GWAS) locus.