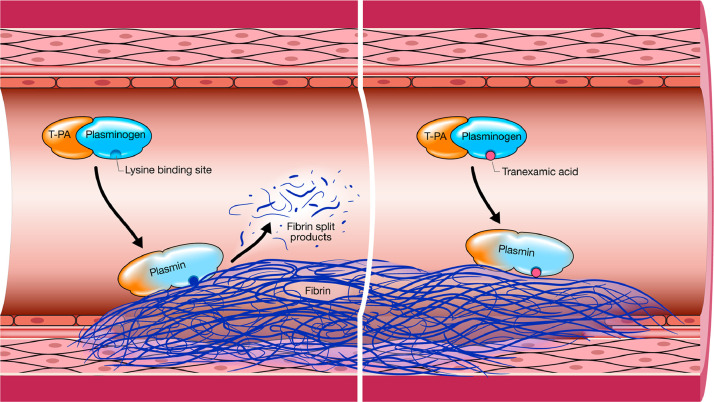
Fig 1.
Depiction of the intravascular cleavage of insoluble fibrin by plasmin thereby releasing fibrin split products, of which D-dimer is one type. The mechanism of action of intravascular TXA is also depicted on the right panel. TXA is a synthetic analog of lysine that reversibly binds to the lysine receptor site on plasminogen to decrease the conversion of plasminogen to plasmin. Used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research.