FIGURE 3.
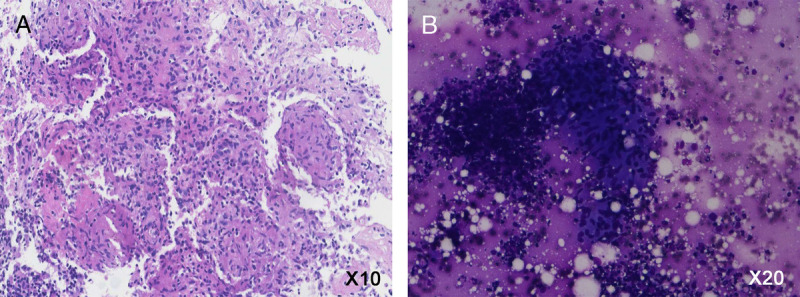
However, biopsy of the left supraclavicular lymph node demonstrated the presence of tuberculosis (TB). Granulomatous nodules composed of epithelioid cells, caseous necrosis, and inflammatory cells or lymphocytes were observed in microscopic section of hematoxylin-eosin stain (A, original magnification ×10) and Liu’s stain (B, original magnification ×20). The 68Ga-FAPI is developed to detect the expression of fibroblast activation protein (FAP).1–3 FAP is an overexpression in more than 90% of epithelial carcinomas and some mesenchymal tumors, and recent studies showed that 68Ga-FAPI might be a broad-spectrum tumor PET agent.4–6 However, high uptake of 68Ga-FAPI was also found in nontumorous lesions, including wound healing, inflammation, fibrosis, and so on.7,8 This case again highlighted that 68Ga-FAPI could gather in nontumorous lesions. Even so, the positive founding of 68Ga-FAPI in extrapulmonary TB lesions indicates that 68Ga-FAPI could serve as a probe in diagnosis and response evaluation of TB.
