Figure 1.
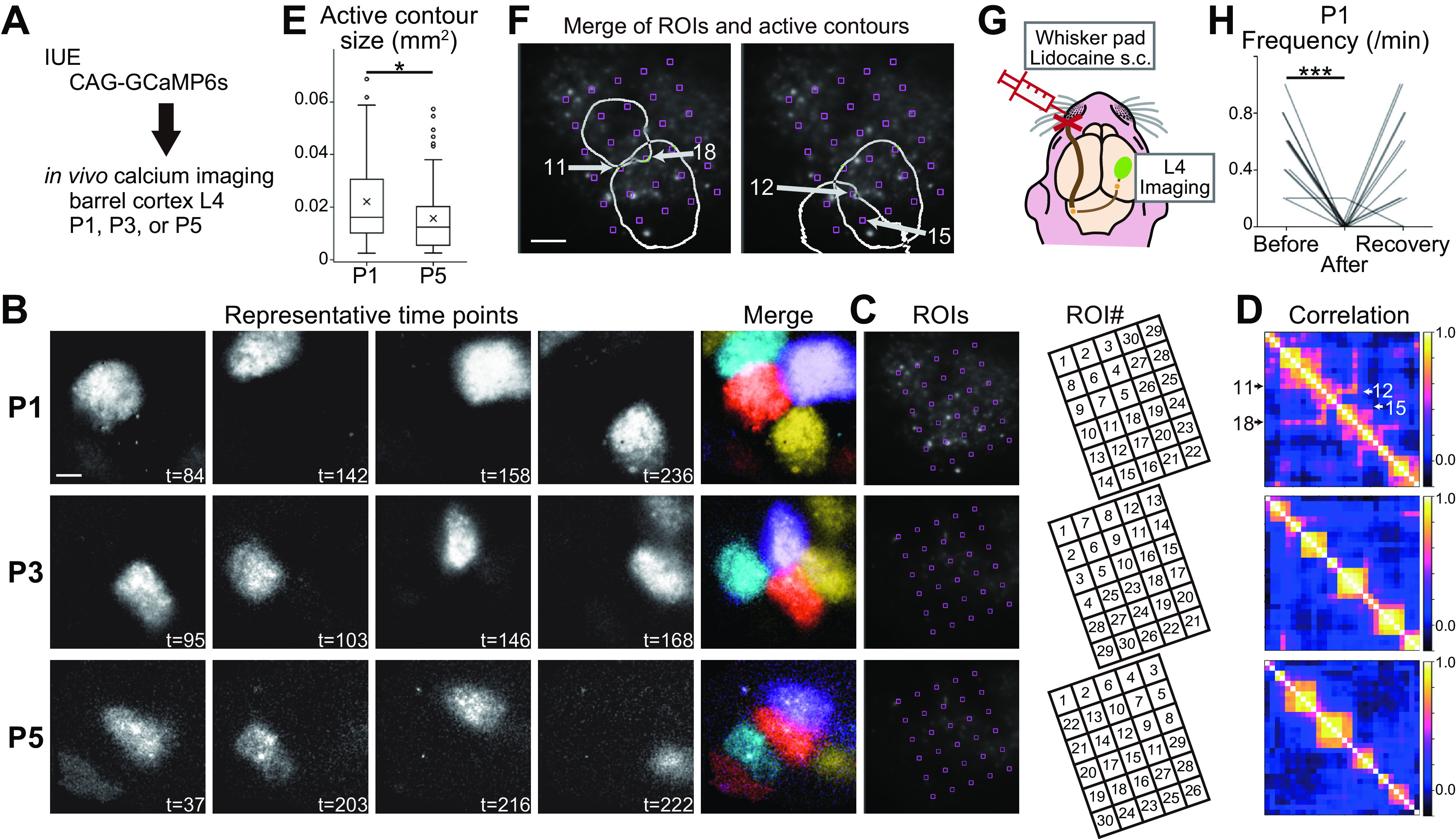
Patchwork-type spontaneous activity observed in L4 glutamatergic neurons of the barrel cortex in the first week of postnatal development. A, Schematic of in vivo imaging with dense L4-neuron labeling. CAG-GCaMP6s plasmid vector was transfected by IUE. B, Representative examples of GCaMP6s signals at P1, P3, and P5. Brightness was adjusted for visualization. See also Movie 1. t, time (in seconds). C, left, ROIs were placed in the barrel field uniformly, because barrels are not visible at P1 yet. Right, ROIs were manually numbered to show the correlation clusters of ROIs in D clearly. D, Correlation matrices of ROI pairs in C. E, Size of active contours at P1 was larger than that at P5. Box plot interpretation is described in Materials and Methods. F, Two examples of overlapping active contours at P1. Arrows indicate ROIs located on overlapping regions of neighboring contours. ROI numbers are the same as those shown in C. G, Schematic of the L4-neuron imaging experiment with peripheral silencing. H, Local anesthetic lidocaine injection into the whisker pad significantly reduced the frequency of L4-neuron spontaneous activity in contralateral side of the barrel cortex at P1. Note that the activity was recovered in 15 min (recovery), suggesting that lidocaine injection did not damage the circuits. B, F, Scale bars, 100 μm. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
