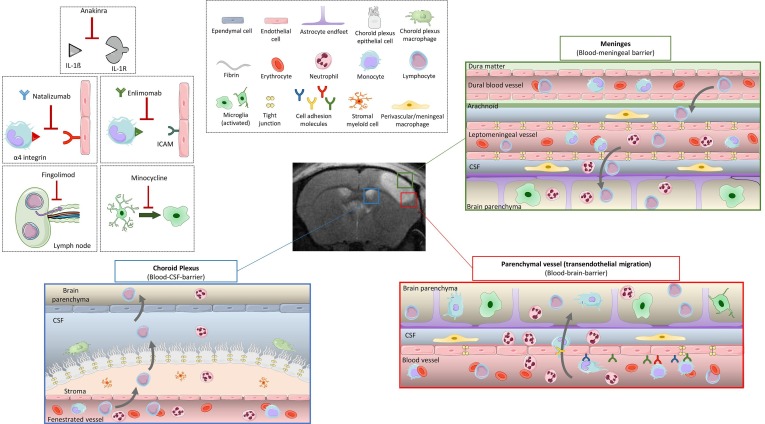
Fig. 1.
Inflammatory/immune responses after ischemic stroke, and targets of the immunomodulatory drugs tested on clinical trials. In the healthy brain, three main barriers protect the parenchyma from external pathogens: the blood–brain barrier (BBB) around the cerebral vessels, the blood-meningeal barrier in the meninges, and the blood-CSF barrier of the choroid plexus. Immune cells circulate freely in the blood, and a few lymphocytes patrol the CSF to do immunosurveillance. In the brain parenchyma resting microglia survey the environment with their processes. After stroke, microglia switches from a resting form to an activated state, adopting a phagocytic phenotype and secreting pro-inflammatory factors. The BBB is disrupted, local ECs are activated and express CAMs. The tight junctions between ECs disappear. This allows leukocyte rolling and adhesion at the luminal side of the blood vessel and then transmigration from the vascular compartment to the brain parenchyma. Leukocytes can also invade the brain through blood-meningeal and blood-CSF barriers. Once infiltrated in the tissue, neutrophils secrete pro-inflammatory factors that will recruit monocytes/macrophages, and later lymphocytes to the parenchyma. Immunomodulatory drugs tested on clinical trials and discussed in this review include (i) Anakinra, an antagonist of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-1, (ii) Natalizumab, which acts by blocking the binding of integrin α4 to the adhesion molecule VCAM to reduce leukocyte infiltration. (iii) Enlimomab is an antibody targeting the adhesion molecule ICAM. (iv) Minocycline inhibits microglial activation among other anti-inflammatory properties. (v) Fingolimod is a high-affinity agonist for several of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors that prevents the egress of lymphocytes from lymph nodes, thus limiting the infiltration of lymphocytes to the brain. BBB, blood–brain barrier; CAM, cellular adhesion molecule; CSF: cerebrospinal fluid; EC, endothelial cell.