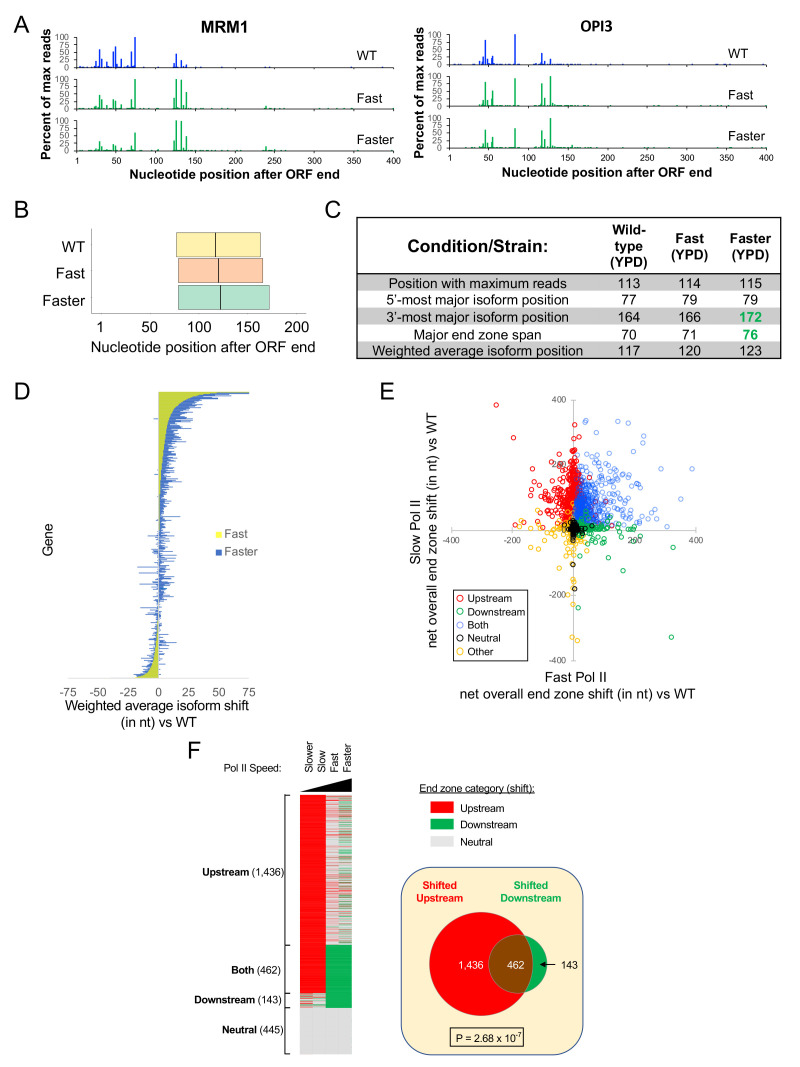
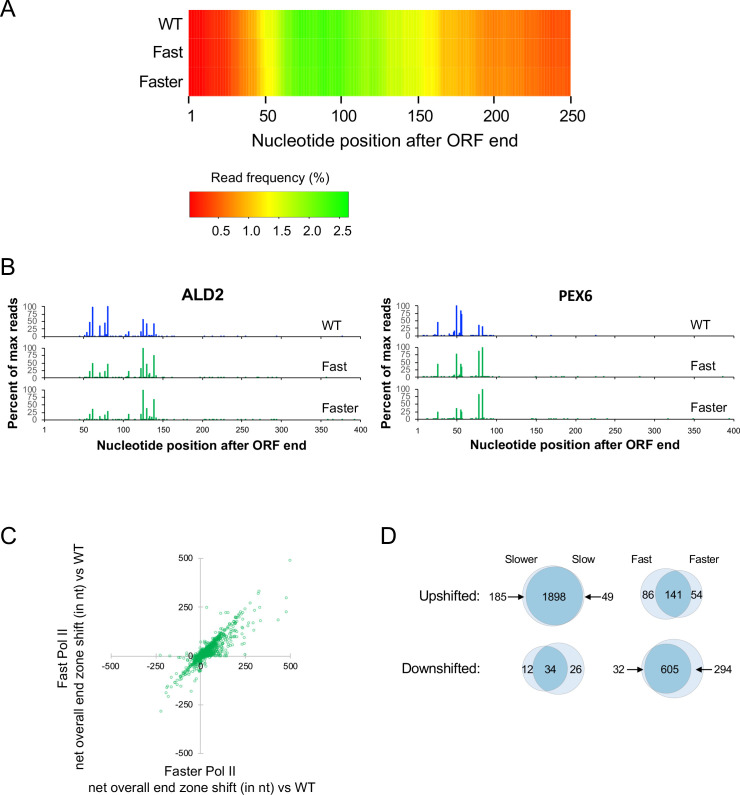
Figure 4. Increased usage of downstream poly(A) sites in fast Pol II strains.
(A) End zone profiles for MRM1 and OPI3 in strains with wild-type, L1101S (‘fast’), and E1103G (‘faster’) Rpb1. (B) Major end zones of these strains. Boundaries represent median values genome-wide for 5’-most and 3’-most major isoforms, and the vertical line within the major end zone represents the genome-wide median of the weighted average isoform position. (C) Table of statistics for landmark positions. Numbers aremedian values across genes with a total of at least 1000 sequence reads in both replicates in every condition. Numbers in bold green are significantly shifted downstream from WT (p < 0.01). (D) Bar graph representation of each gene’s net shift in weighted average isoform position in strains with fast vs wild-type Rpb1. Each horizontal line represents one gene, ordered by shift values in the ‘fast’ strain; the graph includes 3627 genes with a combined read count of at least 1000 for both replicates in all three strains. Yellow represents the 'fast' strain and blue the 'faster' strain, with the overlap appearing green. To obtain net shift values for every gene in each mutant strain, the average shift vs WT in two replicates was diminished by the absolute value of the average shift of the WT and mutant biological replicates. The net shift was set to zero if the absolute value of the shift vs WT was less than the absolute value of the shift between biological replicates. (E) 2790 genes are plotted as a function of the average overall net end zone shift (see Materials and methods) in either catalytically fast (x-axis) or slow (y-axis) Pol II mutants. Genes were classified into Upstream (red), Downstream (green), Both (blue), Neutral (black) and Other (orange) on the basis of each gene’s net end zone shift (see text). The upper right-hand quadrant comprises genes shifted upstream in slow Pol II mutants and downstream in fast Pol II mutants, while genes in the upper left-hand quadrant are shifted upstream in both fast and slow Pol II mutant strains. The bottom right quadrant contains genes that are shifted downstream in both slow and fast Pol II mutants, while the few genes whose end zones are shifted downstream in slow Pol II and upstream in fast Pol II strains are found in the bottom left quadrant. (F) Left: Classification of genes by category. The categories are: ‘Upstream,’ genes whose poly(A) sites were upshifted in both slow-Pol II strains; ‘Downstream,’ genes whose end zone profiles were downshifted in both fast-Pol II strains; ‘Neutral,’ genes with no end zone shift in any slow or fast Pol II-containing strain; and ‘Other,’ genes with any other combination of properties (see Materials and methods). Right: Venn diagram illustrating the 'Both' sub-category of genes (see Materials and Methods), i.e. the intersection of the set of genes shifted upstream in slow Pol II (Upstream category) with the set of genes shifted downstream in the presence of fast Pol II (Downstream category).