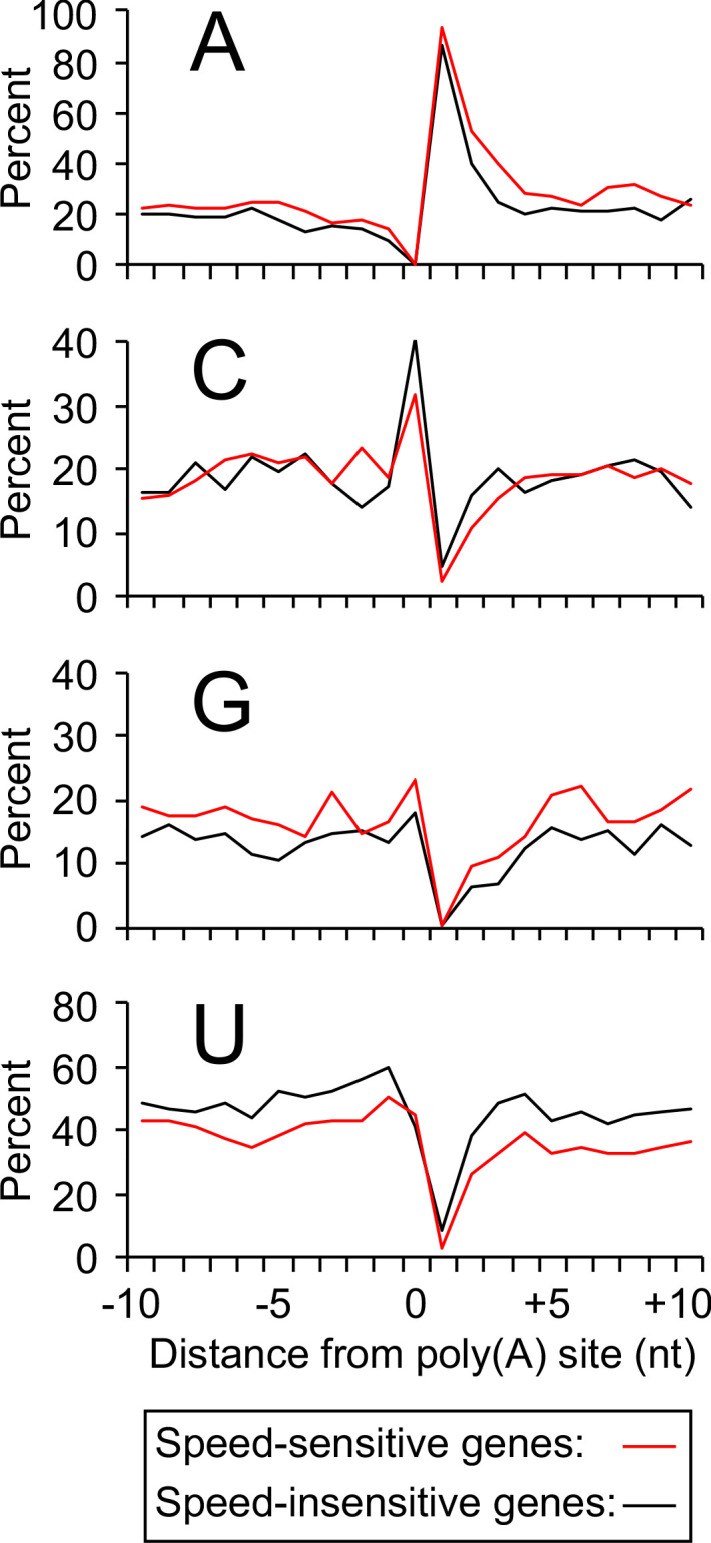
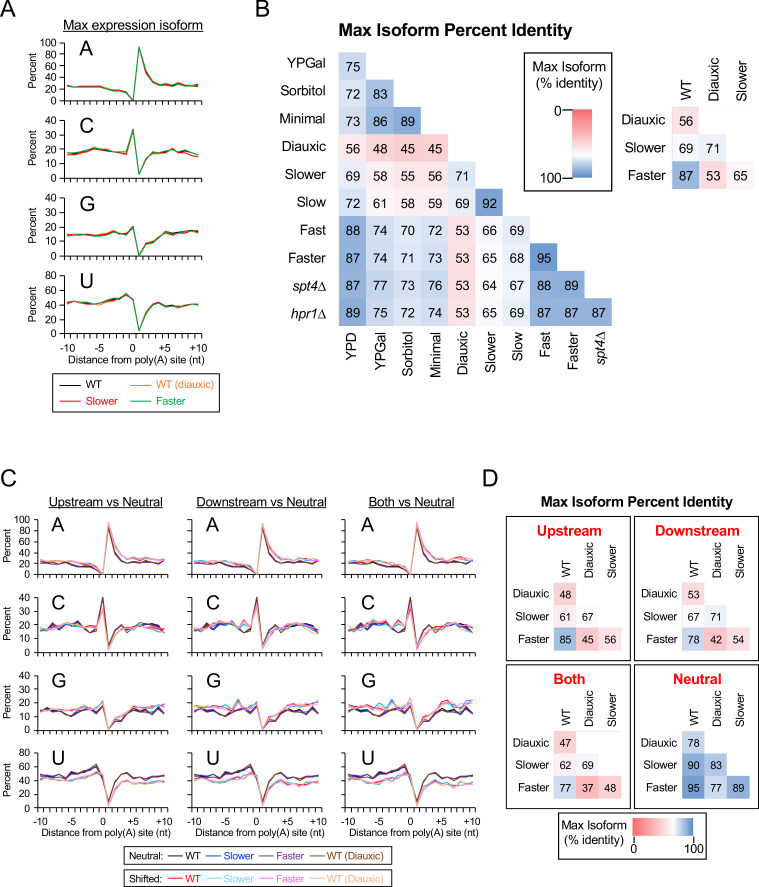
(A) Nucleotide frequencies near max isoform poly(A) sites in strains with WT Rpb1 (exponential and diauxic cultures), Rpb1 H1085Q (‘slower’), and Rpb1 E1103G (‘faster’). Frequencies are shown for the 2790 genes with ≥1000 reads in the 11 conditions described in the paper. (B) Percent identity of max isoform coordinates in the indicated conditions/strains. The analysis was performed on 2790 genes with over 1000 reads (combined from both replicates). (C) Comparison of nucleotide frequencies near max isoform poly(A) sites in distinct subsets of yeast genes. (D) Pairwise percent identities of max isoform coordinates for wild-type (exponentially-growing and diauxic), slower-Pol II (Rpb1 H1085Q), and faster-Pol II (Rpb1 E1103G). Max isoform identity percentages are shown for the three major groups (Upstream (1898 genes), Downstream (605 genes), and Neutral (445 genes)) as well as the Both sub-category (462 genes).