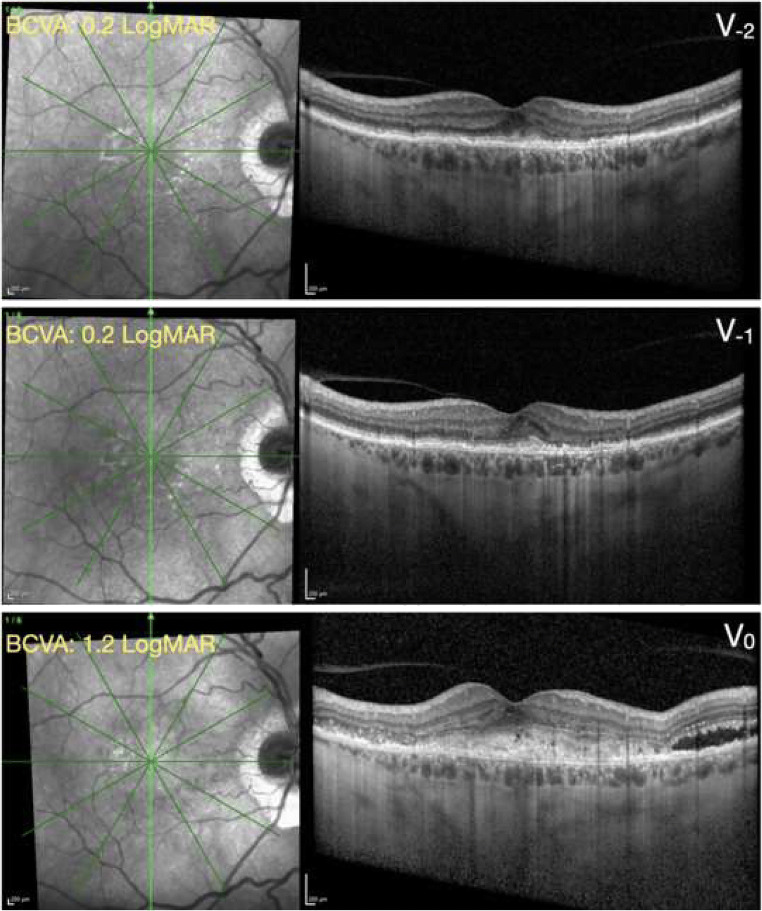
Fig. 4.
Structural OCT from a patient with exudative neovascular AMD. Top panel, V−2 visit; middle panel, V−1 visit; bottom panel, V0 (inclusion) visit. The green arrows on the near-infrared reflectance images (left) shows the location and direction of the structural optical coherence tomography (OCT) B-scans (right images). At the V−2 and V−1 visits, the structural OCT B-scans show the presence of a fibrovascular pigment epithelial detachment associated with a small amount of subretinal hyperreflective material (SHRM). At the inclusion visit performed during the COVID-19 pandemic (V0), the structural OCT B-scan displays an increased quantity of SHRM with associated subretinal fluid. Similarly, the best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was significantly worse at the V0 visit, as compared with both the preceding visits (V−1 and V−2). The time interval between following visits was 63 (within V−1 and V−2) and 147 (within V0 and V−1) days