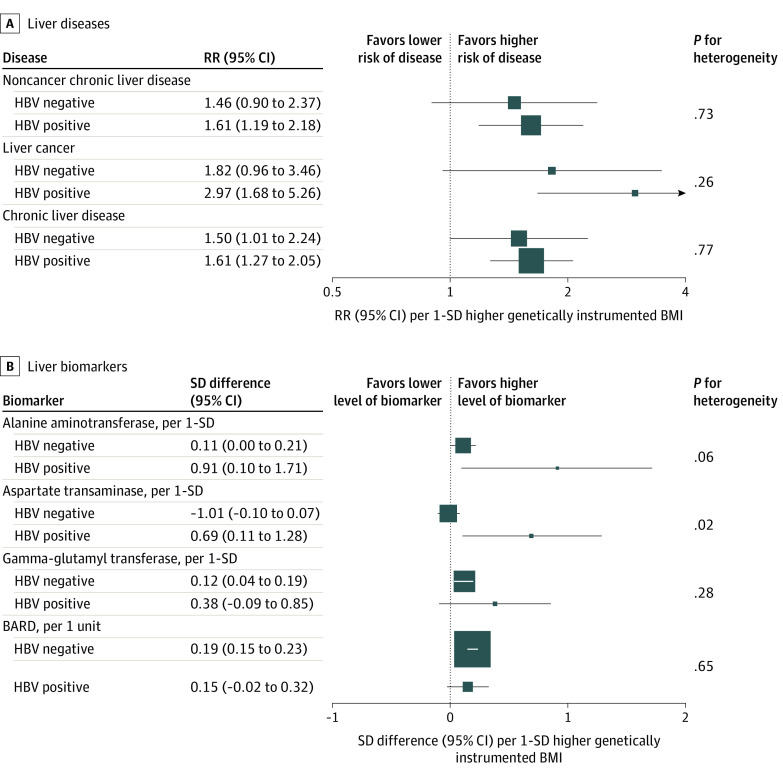
Figure 1. Genetic Associations With Body Mass Index by Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Status.
A. Boxes indicate the relative risks (RRs) of liver diseases associated with 1-SD greater genetically determined body mass index (BMI; calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) in participants stratified by HBV status, with the size of the box inversely proportional to the variance of the log RR. B. Boxes indicate the SD differences of liver biomarkers associated with 1-SD greater genetically determined body mass index (BMI) in participants stratified by HBV status, with the size of the box inversely proportional to the variance of the SD difference. The genetic analysis was adjusted for age, age squared, sex, region, the first 12 principal components, education level, smoking history, and alcohol consumption. P values for comparison were obtained from a Cochran Q test comparing the observational and genetic estimates.