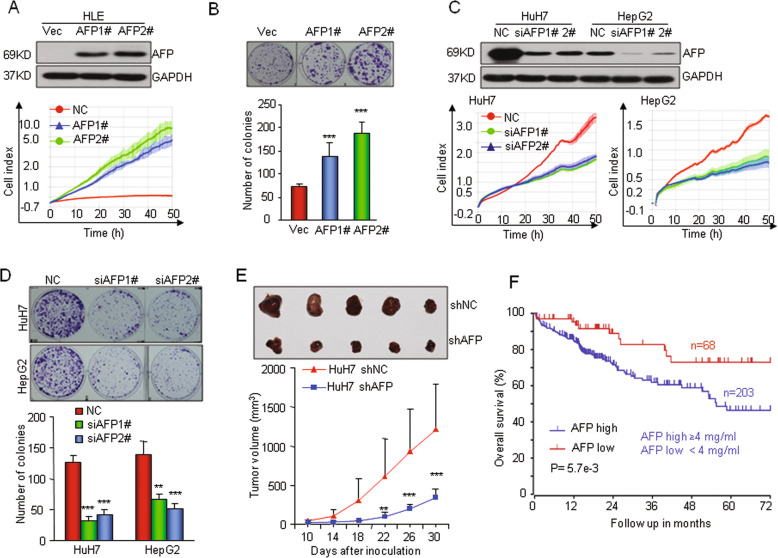
Fig. 2. AFP promotes human HCC cell proliferation in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo.
a Ectopic overexpression of AFP promoted HLE cell growth. HLE cell lines with stable AFP expression (AFP1# and AFP2#) were established and verified by Western blotting (top). Cell proliferation was monitored by an RTCA assay. b Ectopic overexpression of AFP increased the clonogenic formation of HLE cells. c–d Knocking down AFP expression in HuH7 and HepG2 cells reduced the capabilities of cell proliferation and clonogenicity. The cells were transfected with a nontarget control (Non) or siRNAs against AFP (siAFP1# and siAFP 2#). e AFP knockdown suppressed tumor growth in nude mice. HuH7 cells were stably infected with a lentivirus containing an shRNA that interfered with AFP expression (shAFP) or a nontarget shRNA (shNC). The lower panel shows the tumor volume changes at 10 days after inoculation. The upper panel shows tumors that were dissected and photographed at 30 days post inoculation (n = 5). f Kaplan–Meier analysis compared the overall survival rates of 271 HCC patients from the TCGA database stratified by their serum AFP concentration. High AFP expression was defined as a serum AFP level ≥ 4 mg/ml. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 versus control.