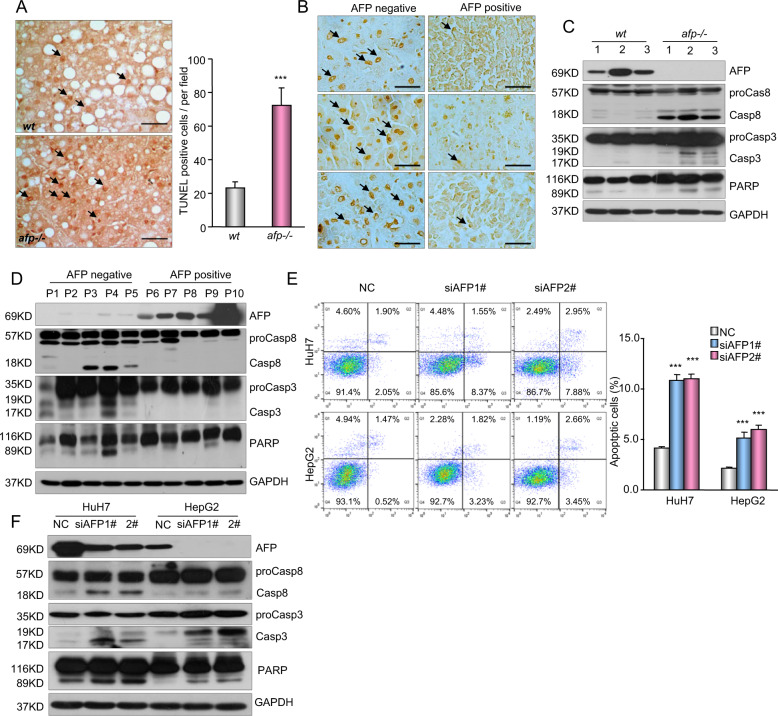
Fig. 3. AFP inhibits cell apoptosis in HCC.
a Cell apoptosis in AFP-positive wild-type (wt) and AFP-deficient (afp-/-) liver tumors from C3H mice was examined by TUNEL staining. Left panel, representative images of the TUNEL assay are shown. Right panel, the frequency of apoptotic cells was calculated and is shown as the mean ± SD of 5 mice per group. Scale bars, 50 μm. ***P < 0.001 versus wt. b Cell apoptosis in AFP-positive and AFP-negative human HCC specimens was examined by TUNEL staining. Data were analyzed and are shown as the mean ± SD of five patients per group. Scale bar, 50 μm. c A Western blot shows the expression of caspase-3, caspase-8 and PARP in AFP-positive wt and afp-/- mouse liver tumors. d A Western blot shows the expression of apoptosis-related proteins in AFP-negative and AFP-positive human HCC specimens. e The effects of AFP knockdown on HCC cell apoptosis were examined. HuH7 and HepG2 cells transfected with a nontarget control (NC) or siRNAs against AFP (siAFP1# and siAFP2#) were analyzed by flow cytometry. Apoptotic cells (%, Q2 + Q4) are reported as the mean ± SD of three replicate experiments. ***P < 0.001 versus the NC. f The effects of AFP knockdown on the activation of caspase-3, caspase-8 and PARP were evaluated. HuH7 and HepG2 cells were transfected with the NC or siRNAs against AFP (siAFP1# and siAFP2#).