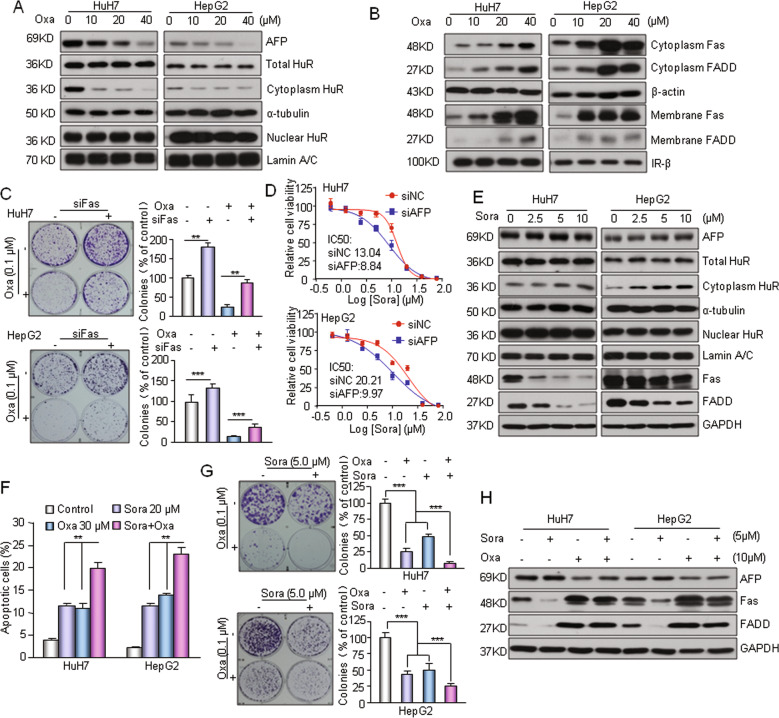
Fig. 7. AFP-mediated cell apoptosis affects the chemosensitivity of HCC cells.
a Oxaliplatin (Oxa) suppressed AFP expression and decreased the distribution of HuR in cytoplasm. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of oxaliplatin for 24 h. b Oxaliplatin activated the Fas/FADD apoptotic pathway in AFP-positive HCC cells. c Knocking down Fas expression attenuated oxaliplatin-induced cytotoxicity. Cell growth was determined by a clonogenic assay. Cells were transfected with siFas or a nontarget siRNA and reseeded in a 6-well plate for 12 h. Then, the cells were incubated with oxaliplatin (0.1 μM) for 40 h and allowed to grow into colonies for 14 days. d Knockdown of the AFP gene in HuH7/HepG2 cells resulted change in sensitivity to sorafenib. The AFP gene was knocked down by siRNA and the viability of cells was assessed by MTT assay. e Sorafenib enhanced cytoplasmic HuR levels and suppressed the activation of Fas/FADD in HuH7 and HepG2 cells. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of sorafenib for 24 h. f Sorafenib combined with oxaliplatin had a synergistic effect on the induction of apoptosis. Apoptotic cells (%, Q2 + Q4) are reported as the mean ± SD of three replicate experiments. g Combination treatment with sorafenib and oxaliplatin synergistically inhibited HuH7 and HepG2 cell growth. Cells were plated overnight, exposed to sorafenib and oxaliplatin individually or in combination at the indicated concentrations for 40 h and allowed to grow into colonies for 14 days. h Oxaliplatin in the combination treatment reversed the inhibitory effect of sorafenib on Fas/FADD activation. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.