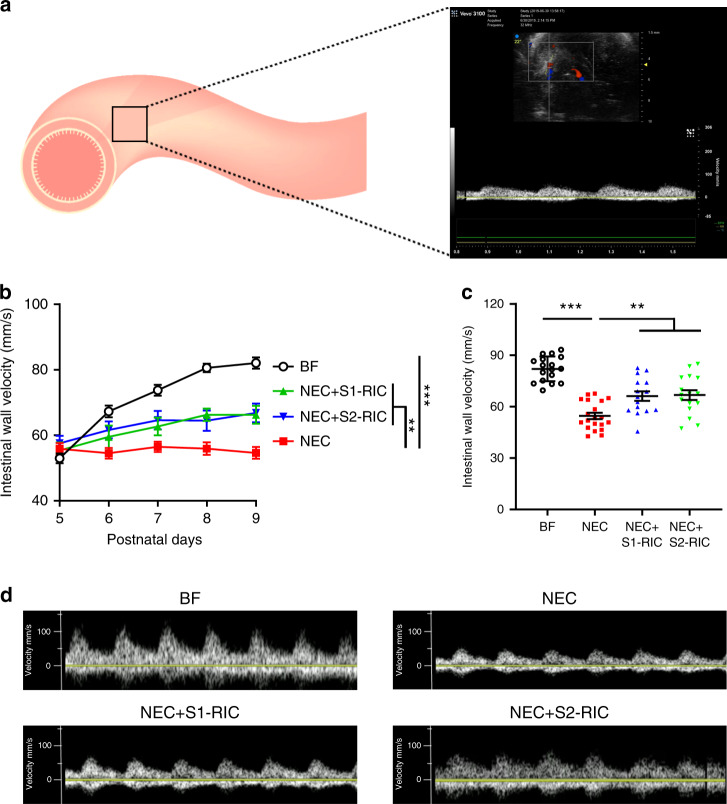
Fig. 3. RIC improves intestinal wall perfusion during NEC development.
a Intestinal wall perfusion was measured using Doppler ultrasound and calculated as average flow velocity (mm/s) of multiple abdominal regions. b Intestinal wall perfusion measured daily from P5 to P9 showed reduced perfusion in NEC pups which was improved following conditioning with Stage 1 or 2 RIC (n = 6 per group; minimum of 3 readings of different abdominal quadrants were obtained per pup; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). c Intestinal wall perfusion measured on P9 in NEC pups showed reduced perfusion compared to breastfed (BF) control, which was preserved in NEC pups receiving Stage 1 or 2 RIC (n = 6 per group; minimum of 2 readings of different abdominal quadrants were obtained per pup; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). d Representative images of arterial waves obtained with the Doppler ultrasound in P9 pups from listed groups. Data were compared using two-sided one-way ANOVA with post hoc Turkey test and data are presented as mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.