Fig. 11.
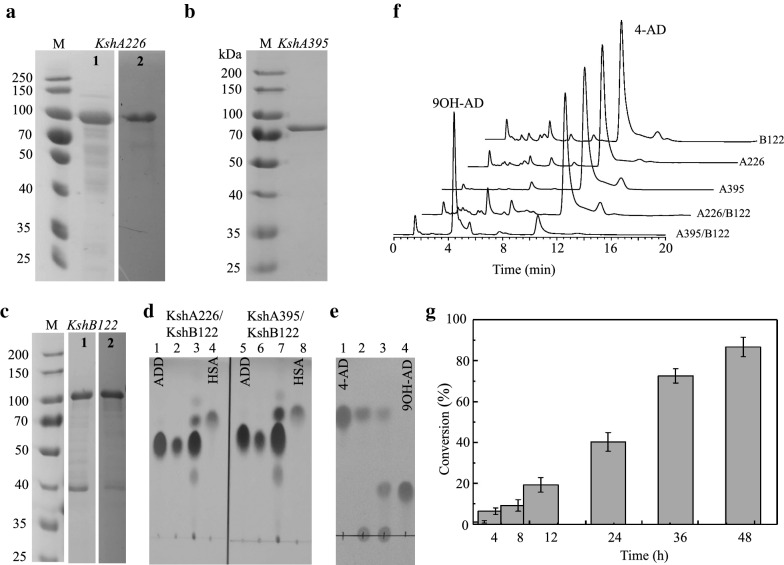
Assay of the substrate conversion catalyzed by KshA226 and KshA395 in combination with KshB122. a–c SDS-PAGE evaluation of purified KshA226, KshA395 and KshB122 fused with MBP. M, Molecular weight markers, which were run on the same gel. In a, sample 2 was run on a different gel simultaneously with the same electrophoresis conditions. In c, sample 2 was run on a different gel simultaneously. d TLC assay of the conversion of ADD to HSA catalyzed by KshA226 and KshA395, respectively, in combination with KshB122. Lanes 1 and 5, ADD standard; lanes 4 and 8, HSA standard; lanes 2 and 6, the reaction mixtures catalyzed by KshA226/KshB122 and KshA395/KshB122, respectively, for 5 h; and lanes 3 and 7, the reaction mixtures catalyzed by KshA226/KshB122 and KshA395/KshB122, respectively, for 20 h. e TLC evaluation of the conversion of 4-AD to 9OH-AD catalyzed by KshA226 or KshA395 in combination with KshB122 within 20 h. Lane 1, 4-AD standard; lane 4, 9OH-AD standard; lanes 2 and 3, KshA226/KshB122 and KshA395/KshB122, respectively, for 5 h; f HPLC assay of the conversion of 4-AD to 9OH-AD catalyzed by KshA226 or KshA395 in combination with KshB122 for 40 h. The peaks for 4-AD and 9OH-AD were marked. g Enzyme-catalyzed conversion of 4-AD to 9OH-AD by KshA395 in combination with KshB122 for 40 h. Error bars indicate standard errors of the means of three repeat experiments