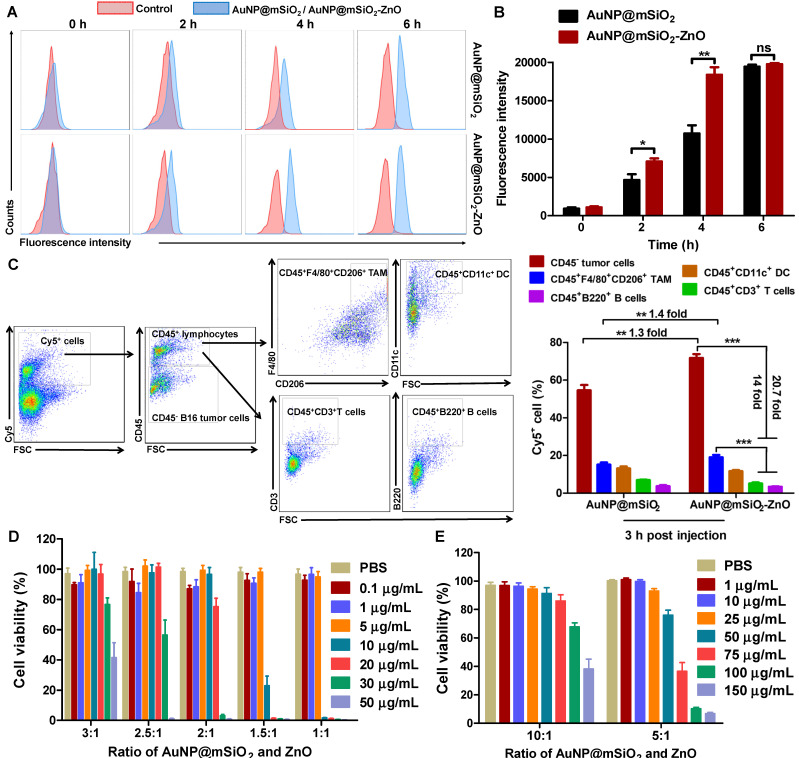
Figure 2.
Uptake and in vitro cell viability of AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO. (A, B) Cellular uptake of AuNP@mSiO2-Cy5 or AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO-Cy5 by B16/F10 melanoma cells in vitro. The cells were incubated for 2, 4 and 6 h, respectively. AuNP@mSiO2 and AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO accumulations, represented by the fluorescence intensity of Cy5, were determined by (A) flow cytometry, and (B) the mean fluorescence intensity. (C) Cellular uptake and internalization of AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO nanocomposite in vivo. The proportions of B16/F10 melanoma cells, TAM, DC, T and B cells that internalized AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO-Cy5 or AuNP@mSiO2-Cy5 were analyzed for 3 h after intratumor injection. (D, E) Cell viability of B16/F10 melanoma cells treated with various concentrations of AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO at different composition ratios of AuNP@mSiO2 to ZnO for 24 h. As the ratio of AuNP@mSiO2 to ZnO was increased, the cytotoxicity of AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO to B16/F10 melanoma cells decreased gradually in a ZnO QDs dose-dependent manner. AuNP@mSiO2-ZnO began to exert cytotoxicity when the ratio for AuNP@mSiO2 and ZnO was 5:1 at 50 µg/mL. Results are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data were given as mean ± SD. The error bars represent the standard deviation. Statistical significance was calculated by the t-test. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. TAM represents tumor-associated macrophages; DC refers to dendritic cell.