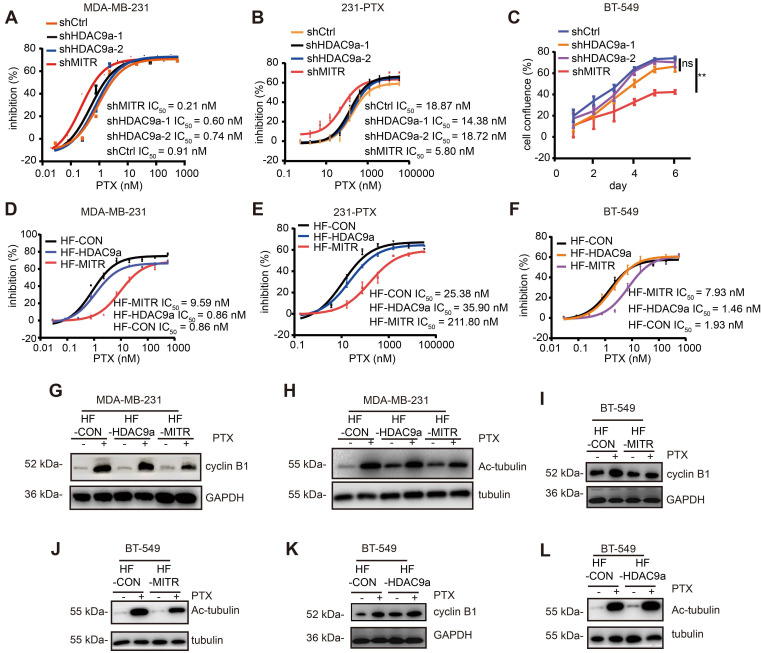
Figure 4.
Truncated HDAC9 isoform (MITR) induced paclitaxel resistance in breast cancer. (A-B) Cell growth inhibition of MDA-MB-231 and 231-PTX cells transfected with shMITR or shHDAC9a, followed by treatment with different paclitaxel doses for 72 h. IC50 values were calculated and compared (shMITR vs shCtrl: p < 0.05, shHDAC9a-1 & shHDAC9a-2 vs shCtrl: p > 0.05). (C) BT-549 cells were transfected by shMITR or shHDAC9a, treated with 1 nM paclitaxel for 6 d, and cell growth inhibition was examined (shMITR vs shCtrl: p < 0.05, shHDAC9a-1 vs shCtrl: p > 0.05, shHDAC9a-2 vs shCtrl: p > 0.05). (D-F) MDA-MB-231, 231-PTX and BT-549 cells stably overexpressing MITR (HF-MITR), HDAC9a (HF-HDAC9a), and empty vector as control (HF-CON), and subject to gradient doses of paclitaxel for 3 d. IC50 was analyzed using Student's two-sided t-test (HF-MITR vs HF-CON: p < 0.05, HF-HDAC9a vs HF-CON: p > 0.05). (G-H) Western blot analysis in MITR or HDAC9a-overexpressed and control MDA-MB-231 cells under paclitaxel treatment, with cyclin B1 and acetylated tubulin antibodies. (I-L) Western blot analysis of cyclin B1 and acetylated tubulin in BT-549 overexpressed with MITR, HDAC9a and control cells treated with paclitaxel.